Uncovertebral osteoarthritis cervical the spine is one of the chronic degenerative diseases. With it, the cartilaginous tissue between the vertebrae is partially destroyed. Osteoarthritis of the cervical vertebrae leads to disruption of the normal movement of the neck and the appearance of various neurological symptoms, since a large number of blood vessels and bundles of nerves.
Chiropractic treatment for osteoarthritis is based on the solution of joint blockade. As a result, stress on already affected joints is reduced and pain relief is achieved. The goal of treatment is to provide the best possible movement between joints that have not yet been affected, in order to prevent wear and tear and to keep the already affected joints as mobile as possible to further reduce wear and tear. However, in the case of chiropractic treatment, not only the directly affected and affected joints are considered, but also tense or even already wrinkled muscles, tendons and ligaments.
What causes arthrosis of the neck?
Osteoarthritis of the cervical spine can be triggered by certain conditions and diseases, which can be both congenital and acquired with age. The most dangerous in this case are abnormalities in the region of 1-2 cervical vertebrae, for example, Olienik's syndrome, otherwise called atlas occipitalization.
can be triggered by injuries in this department, poliomyelitis, dislocation of the head of the hip bones and flat feet. Overweight, physical inactivity (insufficiently active lifestyle), physical activity with uneven lifting of heavy objects, etc. also have a significant effect on the appearance of this disease.
Treatment of surrounding structures is differentiated by stretching between passive and active stretching. The passive form of stretching is performed by a chiropractor, but the patient must maintain the treatment with daily stretching exercises to achieve a satisfactory result.
However, the most important challenge for a chiropractor in osteoarthritis is to diagnose and treat joint changes early before they lead to osteoarthritis. In theory, arthrosis can occur on all joints of the body. In practice, however, we find that arthritic changes in the knees, hips and hands, especially in the most extreme joints of the fingers and at the root or base thumb are the most common in their daily life.
What changes occur in the spine
With arthrosis of the neck, first of all, the intervertebral disc is destroyed, consisting of cartilaginous tissue and performing the function of a shock-absorbing pad between the vertebral bodies, which, in addition to the above, protects the vessels, nerves and muscles.
As it develops, arthrosis thinns the cartilaginous tissue between the vertebrae, the fluid content in it decreases and, accordingly, the cartilage becomes not elastic enough to function normally. Simultaneously with the thinning of the cartilage, the formation of osteophytes (bone growths) occurs on the vertebrae adjacent to the cartilage. Osteophytes grow towards each other. Vertebral arthrosis of the neck is also accompanied by calcification of the ligaments in this part of the spine, which makes them less strong and elastic.
Due to the loss of elasticity, the intervertebral disc begins to protrude forward and backward, thereby squeezing the ligaments that restrict it, and other surrounding tissues. These processes lead to the fact that the symptoms of the disease become noticeable. The first of all the symptoms of vertebral arthrosis is pain in the cervical spine.
Patients with arthritis should go through more than once a week under the supervision of a specialist. The aim of the training is to strengthen the muscles in general, but especially on the worn out joints. However, it is important to ensure that the exams are not too difficult, but not too easy.
In the case of conventional forms of joint pain treatment in Germany, patients are discharged after prolonged, usually unsuccessful treatment with a diagnosis of arthrosis. For patients, this is a shocking diagnosis. However, patients should remember that pain often has a less destructive cause. But even if the diagnosis is confirmed on X-rays, it remains to be said that in most cases of osteoarthritis, the symptoms can be alleviated or even completely eliminated with chiropractic care.
Symptoms
Pain syndrome with arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae is ahead of all other symptoms, it appears already at the very beginning of the disease. In this case, the pain is very intense, it appears locally in that part of the spine that is most close to the affected area. This is due to the fact that the protruding intervertebral disc compresses the ligaments rich in nerve endings, which is why the muscles in the area of the affected cervical vertebrae reflexively strain. Prolonged presence of muscles in a state of spasm leads to an even greater deterioration in the ability to move the neck.
At the initial stage, pain symptoms appear from time to time. They can be provoked by sudden movements of the neck (head turns or tilts), as well as lifting heavy objects.
At this stage, vertebral arthrosis of the neck is easy to defeat; one to two weeks is quite enough to correct the damage that has occurred. If treatment is not started during this period, then later arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae will need to be treated much longer, and the treatment process will be much more complicated.
Subsequent protrusion of the discs causes instability in the cervical spine. Instability of the cervical spine in vertebral arthrosis manifests itself in the form of periodic subluxation of the joints of the facet processes, accompanied by dull severe pain in the affected vertebrae, as well as discomfort in this area of the spine during head turns and at rest. Moreover, if you stay in one position for a while, then the pain and discomfort become stronger. Therefore, to alleviate pain, patients try to change the position of the neck as often as possible. You can do gymnastics or walk around.
Symptoms (pain and discomfort) can disappear both on their own and during a manual therapy session. The restoration of normal functioning of the vertebrae and intervertebral joints is indicated by a characteristic click, after which the pain disappears.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the cervical spine also include a strong crunch in this area of the spine during head turns and extension-flexion of the neck joints.
With a sufficiently pronounced protrusion of the intervertebral discs, hernial formations can squeeze nearby blood vessels and nerve roots, due to which the patient develops various neurological symptoms. Vertebral arthrosis manifests itself in neurology as follows: pains appear in the chest and chest, blood pressure "jumps", vision deteriorates, dizziness, headache, feeling of unsteadiness and instability appear.
Disease of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar spine is one of the most common diseases of the spine. This is usually caused by degenerative changes. In rare cases, however, a traumatic herniated disc may occur during an accident. In the case of a disease of the intervertebral disc, dislocation of the tissue of the intervertebral disc occurs, which can then press on the nerve tissue in the region of the spine.
Typical symptoms of a herniated lumbar disc. Therapy for lumbar disc prolapse is highly dependent on clinical symptoms. If, on examination, in most cases of paralysis or bladder insufficiency is sufficient, then sufficient conservative treatment... These are usually physical maintenance, administration of pain relievers, physical therapy, and physiotherapy.
Establishing diagnosis
 First of all, by asking questions, the doctor finds out what symptoms the patient has. Then an examination is carried out, in which, by identifying painful points, the doctor establishes the localization of muscle spasms. However, this is not enough to diagnose vertebral arthrosis. As a rule, an MRI or X-ray is prescribed to examine the cervical spine. On the images obtained, the specialist will see osteophytes in this section of the spine, signs of vascular and ligament damage near the diseased cervical vertebrae.
First of all, by asking questions, the doctor finds out what symptoms the patient has. Then an examination is carried out, in which, by identifying painful points, the doctor establishes the localization of muscle spasms. However, this is not enough to diagnose vertebral arthrosis. As a rule, an MRI or X-ray is prescribed to examine the cervical spine. On the images obtained, the specialist will see osteophytes in this section of the spine, signs of vascular and ligament damage near the diseased cervical vertebrae.
However, it should be borne in mind that these procedures are invasive methods that carry the risk of nerve damage and spinal inflammation. Operative treatment disc disease is justified in case of unbearable pain or lack of improvement in symptoms of conservative treatment. Paralysis or dysfunction of the bladder and rectal bowel is considered an urgent surgical indication to enable the restored nervous system as soon as possible.
Working methods are different all over the world. The most commonly used and particularly safe procedure is open microsurgery. The incision of the intervertebral disc is removed with a small incision under a surgical microscope. In younger patients, it is also possible, under certain conditions, to implant an artificial disc in the lumbar spine.
Therapy
Treatment of arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae in most cases takes place on an outpatient basis, that is, not in a hospital, but at home. The main goal of therapy (especially in the acute stage) is to relieve pain and provide muscle rest in the area of damaged cervical vertebrae, since during an exacerbation, pain increases due to movement.
To reduce the motor activity of this part of the spine, for example, a Shants collar is used, which fixes the neck well and relieves the maximum load from the cervical vertebrae and adjacent muscles. When the exacerbation subsides, it is necessary to gradually restore physical activity and begin treatment with the help of light massage and exercise therapy.
The hospital stay after such an operation lasts an average of 3-7 days. Patients can usually get up early the day after surgery and go to the toilet and eat while sitting on their own. According to a clinical study, 90% and four weeks after surgery, 95% of patients reported a significant improvement in symptoms. Deterioration or complications associated with surgery should be expected to be less than 1%. In patients who cannot be anesthetized due to other medical conditions, it is also possible surgery in local anesthesia.
Pain medications
Treatment of such a disease as vertebral arthrosis cannot be imagined without pain relievers. Typically, your doctor will prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (known as NSAIDs). These medicines include naproxen, celecoxib, diclofenac, and nimesulide. You cannot take them on your own, since the drug and its dosage must be selected individually. This is due to the fact that some of the NSAIDs, simultaneously with a decrease in inflammation and pain, can negatively affect the metabolism in the cartilage tissue and, accordingly, aggravate vertebral arthrosis of the neck and complicate treatment.
If muscle spasms in the cervical spine are extremely strong and do not go away on their own, then muscle relaxants are used. Drugs in this group allow spasmodic muscles to relax. An example of such medicines is sirdalud.
Similar to prolapse of the lumbar vertebra, the causes of prolapse of the intervertebral disc in the cervical spine are predominantly degenerative. Here, accidents also occur in isolated cases. Typical symptoms of a cervical disc. This leads to impairments in the mechanism and coordination problems in the legs. ... The diagnosis of a herniated disc usually occurs today with nuclear spinal imaging of the lumbar spine. In some cases, however, additional examinations are also required for computed tomography or contrast media analysis.
Other types of treatment
Since arthrosis of the neck causes a malnutrition of the cartilaginous tissue of this part of the spine, drugs are introduced into the treatment complex aimed at restoring microcirculation in the tissues, and antiplatelet agents. For example, courantil, prodectin, actovegin and pentoxifylline.
It is important to include in medical complex and chondroprotectors that help the cartilage tissue of the affected cervical vertebrae to recover. The main drugs in this group are chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine.
Arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae can be stopped or reversed with physical therapy. Treatment with sinusoidal modulated currents, phonophoresis, amplipulse therapy, electrophoresis with a solution of analgesics (lidocaine or novocaine), and magnetotherapy is popular. During remission, exercise therapy and acupuncture have a good effect.
Similar to lumbar disc prolapse, significant improvement in symptoms can be achieved with conservative treatment with physical therapy, physiotherapy measures and, if necessary, pain relievers. In the absence of improvement with conservative treatment, it is necessary to carry out paralysis or cervical myelopathy, to carry out surgical treatment. Unlike the lumbar spine, the cervical spine is usually operated anteriorly to avoid any pressure on the spinal cord.
pozvonkoff.ru
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine: when is disability given?
What is arthrosis? This is the wear and tear of the cartilage tissue inside the joint. The wear of the tissue leads to the emergence of several types of diseases, which are united by one name - deforming arthrosis. Disability with arthrosis can threaten any patient. There are several types of this disease:
The damaged disc is completely removed and replaced with a plastic or titanium spacer. In younger patients with sufficient mobility of the affected disc, implantation of a disc prosthesis is recommended. This is intended to reduce mechanical stress on adjacent discs by maintaining mobility.
Currently, the University Clinic of Neurosurgery in Magdeburg has more than 10 years of experience in the implantation of intervertebral disc prostheses, which has also been documented in a number of scientific works. Spondylolisthesis is a special form of spinal instability that affects approximately 7% of the population and which predominantly affects the lumbar spine. This leads to slipping of the vertebra with the entire overlying vertebral column opposite the main vertebra in different manifestations.
- Primary. Most often, it affects people who are already 40 years old. It can develop in several joints at the same time.
- Secondary. Usually depends little on age. Occurs after injuries or surgeries. Most often, people suffer from secondary arthrosis, on whose legs are very heavy physical exertion.
- Polyarthrosis. As a result of this variety, all joints are affected.
What is the danger of deforming arthrosis? The fact that at first the disease does not cause any pain... They appear later, when the cartilage tissue is already partially worn out. But even then, pain initially occurs only during exertion, and at rest, the joints may not bother.
Moving forward and backward is possible. In the more common forms of Ventrol, there are four Meyerding levels of severity. Basically, there are two forms of spondylolisthesis. All age groups can be affected by patients, and all degrees of severity are possible. This leads to a change in the angle of the vertebral joints as a result of wear of the intervertebral disc and vertebral joints, which makes possible the displacement of the articular surfaces and, consequently, the displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other.
- Pseudospondylolisthesis: This describes a degenerative form of stealth.
- Degenerative listeria predominantly affects elderly patients.
Treatment of deforming arthrosis today is symptomatic. Doctors may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, and in more severe cases, joint replacement surgery. Sometimes, when the patient's condition does not improve, he may be given a disability.
Depending on where the deforming arthrosis begins, several types of ailment are distinguished:
Especially in the case of pseudospondylolisthesis, both pathologies are closely related and usually occur together. Back pain, especially with prolonged standing and walking, shortens the walking distance from pain, numbness, and heaviness in the legs. Standard diagnostic techniques include magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, myelography, and x-ray imaging of the lumbar spine.
In the case of milder forms of vortex slip, conservative treatment may be sufficient. Physiotherapy with strengthening of the abdominal and back muscles, as well as overweight patients - weight loss in the foreground. Swimming training seems to be helpful.
- Deformation knee joint.
- Cervical arthrosis.
Each of these diseases has its own causes, consequences and predictions.
With arthrosis hip joint disturbances in cartilage tissues begin imperceptibly. The symptoms of coxarthrosis can develop for several years. Most often it happens that when a patient comes to see a specialist, the disease is in an advanced stage and requires very great efforts to cure.
Wearing a corset can also ease discomfort. If conservative measures fail to achieve sufficient weight loss or persistent neurological disorders, surgical treatment is necessary. In spondylolisthesis vera, as a rule, stabilization of the affected spine is necessary. In this process, two vortices sliding away from each other are screwed in at the back, and additional "stabilizers" are inserted into the disk drive bay from the front or back. They can be made of bone, bone, or plastic.
In the case of pseudospondylolisthesis, which predominantly affects elderly patients, often less complex surgical procedures are sufficient due to the often lesser form of the sliding stage. Our own clinical studies have shown that in about 80% of cases, minimal significant reduction in symptoms can be achieved with minimal invasive bone decompression of the spinal canal.
Today, deforming arthrosis of the hip joint overtakes more and more young people. One of the reasons for this is the limitation of motor loads. Computers, washing machines, the availability of cars have led to the fact that people move less every year. Their joints do not experience the necessary load, they begin to collapse.
This is a degenerative disease spinal column occurring with advancing age, usually after a year of life. The causes of bone spinal stenosis in parts are unclear and individually different. It is argued that due to age-related water loss on the discs of the intervertebral discs, the height of the intervertebral disc decreases and, as a result, the instability of the spinal column. In response to this instability, reactive formation of bone pores and articular clots occurs.
Bone narrowing of the spinal canal can affect all areas of the spine, but occurs in the lumbar spine and to a lesser extent in the cervical spine. On the thoracic region, they are rarely affected. The appearance of bone stenosis of the spinal canal is similar to the occurrence of other degenerative diseases of the spine. Depending on the localization.
Another reason is completely opposite to the first. Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint threatens athletes, workers whose main physical activity is on the legs.
Other reasons for the development of coxarthrosis include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- congenital dislocation;
- trauma;
- inflammation in the hip joint;
- diseases that lead to the development of secondary arthrosis of the hip joint.
- Malfunction of the legs with a bend of the head.
- Magnetic resonance imaging Computed tomography Myelography.
In the lumbar spine, minimally invasive decompression of the spinal canal under a microscope occurs through a small skin section on the back. In rare cases, stabilization of the spinal column is necessary. The operational risks and duration of inpatient treatment are similar to those of the lumbar spine.
Most often, with this diagnosis, patients complain of pain. However, the moment of its occurrence, localization, intensity are so different in all patients that it is impossible to make a diagnosis based only on the patient's complaints. The doctor will have to conduct a number of studies. And yet, there are common symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint. Among them, the most common are:
- Painful sensations. At the very beginning of the disease, they may be absent, later - they appear only under heavy loads. At the peak of the disease, pain follows the patient even in a state of immobility and rest.
- With arthrosis of the hip cartilage, mobility is gradually limited in the affected joint. The patient can hardly move his legs, often limps.
- Deforming arthrosis gradually leads to a shortening of the leg. Naturally, because of this, the patient's gait changes greatly.
- The muscles on the sore leg gradually weaken, and their atrophy begins.
At the first stage of the disease, the pain is concentrated during exertion in the hip joint, but quickly disappears after rest. On the second, the pain is so strong that when walking you have to move the hip to the side. The third stage threatens with shortening of the sore leg. Patients usually cannot move without a cane.
With arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis), as well as with arthrosis of the hip joint, there is a gradual destruction of cartilage, but only in the knee area. The primary form of the disease can develop from childhood. The reason may be a congenital pathology, insufficient or, conversely, too high load on children's feet, incorrectly chosen shoes.
The causes of the secondary form of arthrosis of the knee joint can be:
- Injuries, dislocations, fractures, ligament ruptures on the legs.
- Operations performed in the area of the knee joint.
- Excessive completeness.
- Diseases accompanied by vasospasm of the legs, convulsions.
- With arthrosis of the knee joint, a violation of metabolic processes in the patient's body is often observed. Some experts argue that it can lead to deformation of the knee joint.
Just like coxarthrosis, deforming arthrosis of the knee joint may not immediately make itself felt. At first, the patient may be disturbed only by mild infrequent pains that occur in the morning when he gets out of bed. This is the first stage of the disease.
Over time, pain appears when climbing stairs, crunching and difficulty in moving. These are sure signs of the second stage of knee deformity. The changes taking place at the last, third stage are noticeable even visually. The patient's legs are bent, practically do not bend at the knees.
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is possible, but requires not only the intervention of a doctor, but also the efforts of the patient himself. Dosed loads on all joints, daily walking, and the absence of bad habits can halt the development of the disease. Patients who are diagnosed with the third stage of the disease may be at risk of disability. It is assigned by MSEC after passing through several stages of special examination.
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine is another type of deforming arthrosis. For various reasons, the patient's vertebrae lose moisture, "sink", the cartilage is worn out and thinned, bone outgrowths gradually grow on the vertebrae. Growing up, they cling to adjacent vertebrae, bringing tangible pain to a person. But pain is not the worst thing that uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine can threaten with. Often, the appearance of bony outgrowths is accompanied by the development of a number of neurological ailments that significantly complicate a person's life. The intervertebral discs become nonplastic, bulge, creating pressure on the surrounding tissue. Unco- or deforming arthrosis of the cervical spine can lead to infringement of nerve endings, disorders of cerebral circulation.
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical vertebra, like other types of arthrosis, can be caused by a congenital anomaly. More often, uncovertebral arthrosis is acquired during life. The causes of the disease may seem frivolous, but it is they that can provoke the development of the disease even in young people and adolescents. What are these reasons? Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine develops if the human body is exposed to constant incorrect dynamic stress. This means that uncovertebral arthrosis of any part of the spine can be caused by:

- improper posture;
- long-term work in a sitting position;
- being overweight;
- improper body position when lifting a load or performing any physical work;
- excessive or insufficient loads on the spine.
Cervical arthrosis can occur after a back or neck injury. It is important to remember that a long time can pass between the injury itself and the onset of the disease.
The diagnosis of "uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine" is made by doctors when the patient's cartilaginous discs dividing the vertebrae wear out and cease to be elastic, and uncovertebral joints form on the back surface of the vertebrae themselves. A healthy person cannot have them, but in a patient they are formed due to the fact that the vertebrae of the cervical spine grow together with the hook-shaped processes that arise during the course of the disease.
Do you give disability with arthrosis, gonarthrosis and arthrosis of the cervical spine?
In order to establish the degree of performance of a patient with deforming arthrosis, the patient is referred to MSEC. Disability of the 1st, 2nd or 3rd degree can be assigned only when this commission establishes the degree of impairment of the patient's static-dynamic functions, which determine his ability to move independently, work and take care of himself. In this case, the symptoms of arthrosis of the cervical spine or limbs (crunching, pain, etc.) are of secondary importance. Disability will be given when the loss of static-dynamic functions interferes with the patient's full life.
MSEC is sent:
- patients with progressive arthrosis, which is confirmed by X-ray images and exacerbations that occur at least three times a year;
- sick after surgical treatment coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis or uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine;
- patients with severe mobility limitations.
At the first (clinical and functional) stage of the MSEC, the patient undergoes a series of studies designed to determine the degree of the disease. At the second stage (social diagnostics), specialists assess the degree of loss of skills of the patient's ability to work and self-care, the level of his social adaptation. Medical experts pay special attention to the physical and psychological state of the patient, his rehabilitation potential. The third stage of this examination is designed to determine the level of the patient's needs for protection and assistance. After that, MSEC determines which group of disabilities will be given to the patient.
Disability criteria

- People with disabilities in this group need constant care, cannot take care of themselves, walk, stand, study or work on their own, and their social adaptation is at the lowest level. Most often, such a disability is assigned with 3-4 degrees of disorders of the knee or hip joint, pronounced uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine. Disabled people of the first group need constant guardianship of outsiders.
- The second group of disability can be assigned in the event that the patient's ability to work, take care of himself or learn is significantly lost and cannot be carried out without outside help or aids. For the work and training of such patients, specially equipped places are required. Most often, the second group is received by persons suffering from arthrosis of the third degree, frequent exacerbations, shortening of the limbs due to illness.
- Disability of the third group can be given to patients whose motor abilities are significantly limited. Such people spend more time on overcoming standard distances, can take care of themselves only with the help of special devices. Their qualifications are reduced or completely lost due to illness.
Disabled people of the third group can engage in light or mental work. Do other cases give disability? Perhaps, but only MSEC decides this.
artrozmed.ru
Features of uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of one or several intervertebral discs and (or) facet joints. Moreover, this can contribute to the development of pathological changes in the anatomical structure of the transverse canal, which often leads to compression or displacement of the neurovascular bundles located in it (sympathetic trunk, vertebral vein and artery).
Reasons for the development of uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
Currently, many conditions and diseases of a person are known, the presence of which, to one degree or another, contributes to the occurrence of cervical arthrosis. They are usually divided into acquired and congenital.
Among congenital pathologies, it should be noted anomalies in the development of the cervical segment of the spine, especially in the region of the I-II cervical vertebra. An example is the Atlantean occipitalization (or Olienick's syndrome).
Of all the acquired diseases that contribute to the development of cervical arthrosis, specialists most often mention:
- Injuries of the cervical segment of the spine;
- Flat feet;
- Dislocation of the head of the hip bone;
- The consequences of poliomyelitis.
Also of great importance in the development of uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine are factors such as:
- Excess weight;
- Physical inactivity (or a sedentary lifestyle);
- Irregular physical activity, including constant weight lifting, etc.
The mechanism of development of the disease
The disease primarily affects the intervertebral disc. It is a kind of elastic "pad" between the nearby vertebrae, consisting of cartilage tissue. Which absorbs during various movements, thereby protecting the vertebral nerves, blood vessels and even muscles passing nearby from possible damage.
Together with the progression of the disease, the intervertebral cartilage tissue also becomes thinner. It gradually loses fluid, as a result of which its elasticity decreases, which is so necessary for normal operation. At the same time, on themselves cervical vertebrae special bone growths, or osteophytes, begin to develop. Moreover, the latter grow on closely spaced vertebrae and are directed towards each other. And in addition to this, the ligaments of the cervical segment of the spine also begin to lose elasticity and strength, due to increasing calcification.
After the intervertebral disc becomes less elastic, it gradually begins to protrude in the posterior and anterior directions, while squeezing the ligaments that limit it and other nearby tissues. And this always leads to the development of the corresponding symptoms of the disease. First of all - this is incessant pain in the neck.
Symptoms of uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
One of the earliest signs of the disease is neck pain. Moreover, it is almost always local (arises exactly where the “problem cervical vertebra is located) and is very strong.
This symptom is due to the fact that the intervertebral discs protruding back and forth strongly press on the surrounding ligaments, which, in turn, are rich in nerve endings. In addition, the muscles in this area are constantly reflexively tense and remain in this state for a long time, and this greatly affects the ability to produce free neck movements.
At the onset of the disease, pains are periodic in nature and are provoked by any sharp movements of the neck (tilts, turns) and excessive weight lifting.
It should be said immediately that by contacting a doctor at this stage of the disease, a person can very quickly (1-2 weeks) eliminate the disorders that have appeared. If treatment is neglected, the disease will continue to progress.
In the future, the disease manifests itself in the occurrence of instability in the cervical segment of the spine. This is evidenced by the increasing incidence of subluxation of the joints between the facet processes. In addition, if a person is in one position for a long time, then the pains begin to intensify. That is why patients with this disease try to change the position of their body often enough in order to somehow mitigate the growing pain. In this they are also well helped by therapeutic walking and gymnastics.
Pain can subside either spontaneously or after manual therapy. Moreover, the termination and restoration of the usual work of the joint is accompanied by a specific click directly in the area of the joint.
Another clear sign of a patient with cervical arthrosis is a strong crunch, which is observed during extension, flexion and rotation of the neck.
You can also read:Dizziness with cervical chondrosis
In addition, arthrosis of the uncovertebral joints can provoke the following symptoms:
- Feeling wobbly and unsteady;
- Dizziness;
- Headache;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Jumps in blood pressure;
- Chest pain.
This is due to the fact that the protrusion of the intervertebral discs becomes more pronounced. And the resulting hernias squeeze the nearby blood vessels and nerve roots.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to correctly establish the diagnosis of "uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine", the doctor must carefully interview the patient. From this, he draws conclusions about the nature of the disease, the causes of its occurrence and the frequency of manifestations. Also, the doctor finds the most painful points in the cervical segment (which tells him about the localization of pathological muscle spasms).
However, the main methods for diagnosing the disease are still all kinds of imaging methods: MRI and X-ray of the cervical spine. They allow the specialist to verify the presence of osteophytes in the vertebrae (coracoid outgrowths) and signs of damage to blood vessels and ligaments in the problem area.
Treatment of uncovertebral arthrosis
Most often, the treatment of this disease is carried out on an outpatient basis. The main goal is to eliminate pain and provide muscle rest in problem areas of the neck. This is especially true of the stage of exacerbation of the disease.
The following methods are used for treatment:
- Decreased motor activity. For this purpose, a Shants collar is used, which fixes the neck and reduces the load on the cervical vertebrae and nearby muscles;
- Preparations for the elimination of pain and muscle spasms. NSAIDs (naproxen, diclofenac, celecoxib, nimesuli) are most commonly used to relieve pain. With strong local muscle spasms, it is recommended to take muscle relaxants (sirdalud, etc.);
- Improving blood flow to the damaged area. To do this, use the following medicines as courantil, actovegin, prodectin or pentoxifylline;
- Drugs that accelerate the restoration of cartilage tissue, or chondroprotectors. The main active ingredients they contain chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine.
- Physiotherapy. Among them, the most effective are:
- Magnetic therapy;
- Electrophoresis and phonophoresis with novocaine or lidocaine;
- Amplipulse therapy;
- Sinusoidal modulated currents.
At the stage of remission (if there is no pain syndrome), doctors recommend acupuncture and physiotherapy.
MoyaSpina.ru
The essence of osteoarthritis of the spine, symptoms and treatment of the disease
Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system are one of the most common today. By the number of visits to doctors, arthrosis of the spinal column occupies a leading position, along with such diseases as osteochondrosis and sciatica. The disease can occur in different ages, but in people over 70 years of age, it is almost always present.
Spinal osteoarthritis is a lesion of the cartilaginous surfaces of the intervertebral joints with the gradual involvement of the vertebral bodies, muscles and ligaments in the process, which further leads to the appearance of pain and limited mobility. The most often damaged cervical and lumbar... The causes, symptoms and treatment of arthrosis in different parts of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar) are very similar regardless of the localization of the process.
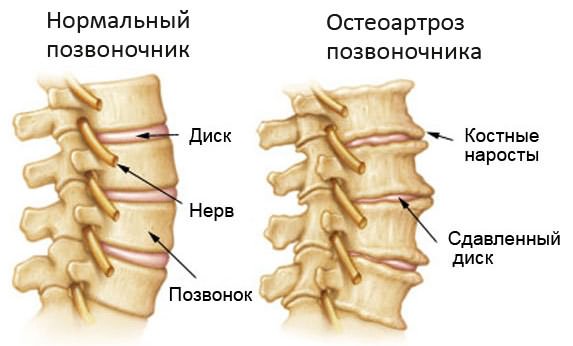
Causes of the disease
Considering that changes in cartilaginous structures develop gradually, often over several decades, arthrosis of the spine is rightfully considered an age-related pathology. The deterioration of cartilaginous structures is the most likely, but not the only, cause of this ailment.
What are the factors contributing to the development of vertebral arthrosis?
Increased stress on the cervical and / or lumbar spine due to the peculiarities of work (for example, seated work with a bowed head or frequent lifting of weights).
Orthopedic pathologies (kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis, flat feet, dislocations and subluxations of the hip joint), in which the total load on the spinal column is not distributed correctly.
Congenital anomalies of the vertebrae (for example, fusion of the first two vertebrae with each other or with the skull).
Inflammatory processes in the spinal column.
Injuries, fractures of the spine.
Herniated discs.
Endocrine diseases and age-related changes (for example, decreased activity of sex hormones).
Metabolic diseases (gout).
Infectious and allergic diseases (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses of the nose or middle ear, tonsillitis).
Environmental factors: hypothermia, especially in combination with high humidity, poor environmental conditions, the use of low-quality water.
The region of residence and the gender of a person also matter. It has been proven that up to 45 years of age men are more susceptible to arthrosis of the spinal column, which is associated with their higher physical activity due to the peculiarities of work or sports. As we approach the age of 50, the number of men and women with osteoarthritis becomes comparable, and at the age of 55–65, women predominate among patients.
It is known that in some regions of the globe this pathology is much more common. For example, in the countries of South and North America, South Africa, the Caucasus, arthrosis of the cervical and lumbar vertebrae is recorded much more often in comparison with Russia and European countries.
What changes occur in the vertebrae in osteoarthritis?
The disease is based on changes in chondrocytes - cells that form cartilage tissue. With a disease in the intervertebral joints, as well as in the intervertebral discs, there is an increased death of cells that produce normal collagen. The remaining chondrocytes produce atypical collagen, which is unable to fulfill its main functions - retaining water and proteins to maintain the elasticity, firmness and shock absorption of the cartilage. The result is impaired mobility of the spine and pain.
Gradually, osteophytes, bone spines, which severely injure the articular surfaces, begin to "grow" inside the joints.
Somewhat later, soft tissue structures (muscles, ligaments) are affected, in which inflammation develops, their tone decreases. Develop visible to the eye deformities of the spine and figure in general.
The term "osteoarthritis" has synonyms: degenerative arthropathy, osteoarthritis (this term emphasizes the presence of local inflammation in the cartilage, bone and muscle structures surrounding the vertebrae). The defeat of osteoarthritis of the cervical spine is often called "uncovertebral arthrosis".
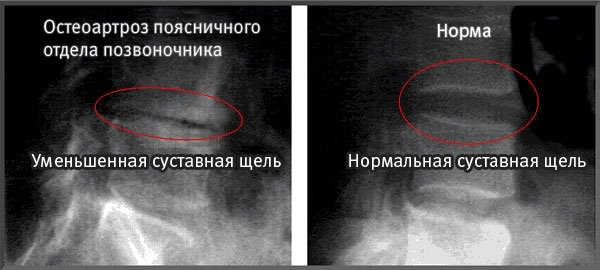
In the photo - an X-ray
The main symptoms
The first symptom that osteoarthritis of the spine manifests itself is pain ... They are of a heterogeneous nature and are caused by various reasons.
- The most common pain is mechanical. It occurs after a hard day, during which a lot of physical stress was exerted on the spine. Discomfort usually goes away overnight.
- Another type of pain - venous, develops mainly in the first hours of a night's rest. The pain is dull, continuous, its cause is stagnation of venous blood in the vessels that feed the vertebral joints.
- Initial pains are short-lived, appear immediately after sleep and last no more than 20 minutes. They pass on their own after the start of physical activity.
- With the progression of the disease, pain becomes permanent - in this case, they are caused by muscle spasm and entrapment of nerve fibers.
Against the background of intense pain, appears limited mobility of the spine ... Other symptoms are gradually added, indicating the progression of the disease: changes in posture, swelling and induration in the area of the affected vertebrae, decreased range of motion in the neck or when turning the trunk.
Osteoarthritis of the cervical spine is also manifested by one-sided pain, which can reach the angle of the scapula, give to the chest or arm. Therefore, patients often come to a cardiologist with suspicion of ischemic disease hearts. Only radiography can reveal changes in the cervical spine, characteristic of arthrosis of the vertebrae.
Make you see a doctor should neck crunch that occurs when turning and tilting the head, possible visual impairment, dizziness, tinnitus, increased blood pressure.
Treatment methods
The earlier the patient applies for medical help, the easier it is to help him. If a patient seeks a doctor at the initial stage of the disease, in which there are still no pronounced changes either on the cartilaginous surfaces of the vertebrae or in the intervertebral discs, an improvement in the condition may occur within a few weeks from the start of treatment.
There are 4 main methods of treatment:
Medication is aimed at relieving pain and inflammation. Analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, hormonal drugs are used. Chondroprotectors - preparations of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine - are used to stimulate regenerative processes in cartilage and intervertebral discs.
Orthopedic treatment with traction and assistive devices (an example of such a device is the Shants collar) helps to relieve the spine and slow down the progression of the disease.
Massage and manual therapy are necessary to restore the correct anatomical shape of the spinal column, restore blood circulation, relieve pain, eliminate muscle spasm, and improve cartilage nutrition.
Therapeutic gymnastics in combination with physiotherapy allows you to eliminate pain, strengthen the muscles of the neck and the entire back, and increase the mobility of the vertebral joints.
During the period of remission, courses of acupuncture, mud or paraffin therapy, hirudotherapy are recommended. Without exception, all patients with arthrosis of the spine should develop the habit of sleeping on a moderately hard bed with a low pillow, monitor their posture during the day and, in general, always keep the torso in correct position... Swimming in the pool is very useful (preferably 2-3 times a week).
Let's summarize
Despite the fact that osteoarthritis is considered almost an inevitable age-related disease, it can be successfully dealt with. For the treatment to be effective, it should be dealt with by a specialist - a vertebrologist who knows all the anatomical and physiological features of the spinal column. Self-medication is categorically unacceptable, since a significant deterioration of the condition is possible, up to the loss of sensitivity and motor activity of certain parts of the body.
SustavZdorov.ru
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine
Uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine is a deformation of cartilage with additional formation of joints on the posterior surfaces of the cervical vertebrae. Because of this, a person can experience various neurological diseases and pain.
The reasons for the development of the disease
This disease can be provoked by hard physical work with an uneven load of severity, improper lifestyle (sedentary work, low physical activity), excess weight, various pathologies of the spine and bone diseases (osteoporosis). Constant pressure on cartilage and joints leads to wear and tear, and as a result, uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical vertebrae develops. Disruption of the thyroid gland can also provoke this disease.
There is a considerable number of concomitant diseases, the presence of which contributes to the development of cervical arthrosis. They are usually subdivided into congenital and acquired. Congenital pathologies include abnormal development of the cervical spine. As a rule, anomalies of the 1st or 2nd vertebra lead to uncovertebral arthrosis. Acquired diseases that involve damage to the cervical spine are spinal injuries, flat feet, hip injuries, and poliomyelitis.
Clinical picture
First of all, the defeat of the intervertebral disc occurs. Then the cartilage tissue becomes thinner, as a result of which its elasticity decreases and normal functioning is disrupted. At the same time, there is an increase in osteophytes towards each other on the vertebrae, between which the intervertebral distance is thinned. This leads to a loss of elasticity of the ligaments of the cervical spine. The affected intervertebral disc begins to protrude, thereby squeezing nearby ligaments and other tissues, including nerve processes. All this leads to the appearance of the first signs of the disease.
The first symptom of arthrosis is a specific crunch during flexion-extension of the joints. Later, pain joins during physical exertion, and in the future, pain will accompany the patient at rest.
The development of uncovertebral arthrosis is also indicated by:
Unsteadiness, feeling wobbly;
Frequent dizziness or headaches;
A sharp decrease in visual acuity;
Sharp jumps in blood pressure.
The appearance of these symptoms is provoked by squeezing of the blood vessels located in the affected area, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain deteriorates.
Diagnosis of the disease
X-rays are used to diagnose uncovertebral arthrosis. It gives a complete picture of the condition of the cervical vertebrae. If, during the examination, the cervical vertebrae look enlarged, the doctor confidently diagnoses uncovertebral arthrosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging can also visualize the presence of osteophytes in the cervical vertebrae, which are coracoid in the image. MRI also detects lesions of the ligaments and blood vessels.
Uncovertebral arthrosis: treatment
In the treatment of uncovertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine, several methods of therapy are used: medication, ultrasound, massage, electrophoresis, thermal applications, physiotherapy exercises. With the help of medicines, doctors relieve pain and inflammation. The use of hormonal agents gives a good effect. In special cases, the patient is shown a spa treatment.
First of all, it is necessary to reduce the motor activity of the patient's neck, for which the Shants collar is used. Relieving tension from the cervical spine helps to eliminate sharp pain.
Drug therapy consists of a complex of drugs that:
- reduce pain and relieve muscle spasm;
- improve blood flow, which is important for restoring normal blood circulation in the damaged area and eliminating headaches;
- stimulate the growth of cartilage tissue. The active components of chondroprotectors are glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
Physiotherapeutic procedures play an important role. The greatest effect can be achieved by conducting sessions of magnetotherapy, electrophoresis and the use of sinusoidal modulated currents.
Reflexology (acupuncture), as well as physiotherapy exercises, are possible only in the absence of pain syndrome, that is, during the period of remission.
Surgical treatment is used only in severe cases.
Can uncovertebral arthrosis be cured? It completely depends on the actions of the patient, because if you promptly seek help from a specialist, attend all the prescribed procedures and strictly follow all the instructions, you can achieve the elimination of pain, and in the future, complete restoration of the cartilaginous tissue.
VekZhivu.com
Symptoms of arthrosis of the cervical spine
In the modern world, more and more people suffer from various diseases that affect the joints of the spinal column, as well as the upper and lower extremities. Previously, such diseases in their overwhelming majority manifested themselves against the background of natural aging processes of the human body or injuries, but now the problem is often caused by a sedentary lifestyle, which is chosen by a person of the technological 21st century. One of the most common diseases is arthrosis of the cervical spine, the symptoms of which we will talk about in this article. This pathology causes deformation of the joints and more fragile cartilaginous joints - intervertebral discs. (See also: uncoverable arthrosis of the cervical spine).
The main problem of cervical arthrosis is that the process of its treatment will always be very protracted, and, unfortunately, no one can give guarantees of complete recovery. The main reason for this lies in the difficulty of obtaining nutrients that the intervertebral disc can only extract from the environment in a diffuse manner. Due to this state of affairs, the doctor does not have the ability to directly influence the joints, so he has to direct the healing effect to the thin tissues located near the lesion.
One can immediately note a unique remedy for the treatment of diseases of the spine, which is highly effective and has many positive reviews.
We are talking about orthopedic plaster "ZB PAIN RELIEF". Large-scale clinical trials were carried out in Stockholm medical university(Sweden) in 2013. In total, more than 1000 men and women with various diseases of the spine and joints took part in them, who used orthopedic plasters "ZB PAIN RELIEF" for 2 weeks. Even doctors were surprised by the research results!
The pains, both acute and aching, disappeared in most of the subjects within 1-3 days after starting to use the patches. More than 70% of those participating in the studies had significant treatment shifts chronic diseases spine and joints.
You can learn more about this patch by following the link below - "ZB PAIN RELIEF".
Factors for the formation of arthrosis in the cervical spine
The main factor responsible for the formation of arthrosis in the cervical spine is the constant heavy load on the joints of the upper spine. As a rule, they are observed against the background of weakening of the cervical muscles, which do not help to carry out the hard daily work of holding the head, bending and turning.
Various injuries, protrusions and hernias of the intervertebral disc can lead to the appearance of cervical arthrosis. In addition, due to a sedentary lifestyle or the processes of natural aging of cells, dangerous inflammatory or dystrophic phenomena often occur, which can also cause joint pathology. It should be mentioned that in some cases, the malfunctioning thyroid gland is responsible for the occurrence of destructive processes.
Signs of arthrosis in the cervical spine
Patients may experience the following symptoms of arthrosis of the cervical spine:
- frequent dizziness;
- morning pain in the shoulder and neck area;
- inability to perform individual movements, as the neck literally "wedges";
- vision problems;
- partial paralysis of the tongue and facial muscles;
- pain in the back of the head and temples, which are difficult to eliminate with conventional pain relievers.
Such symptoms can be the result of not only cervical arthrosis, but also many other diseases, so it is extremely important that an experienced specialist makes the diagnosis after a thorough examination. Actually, in order to establish the presence of arthrosis of the cervical spine, it is enough to conduct an MRI, but concomitant disorders are possible, which should also be identified as soon as possible and accurately.
It is very important to deal with the treatment of arthrosis in a timely manner, as it can lead to:
- compression of the vertebral artery;
- pinching of nerve fibers.
How to cure cervical arthrosis
The course of treatment is different an integrated approach and the first thing the doctor must do is to eliminate pain. For this, drug therapy is prescribed, within which the patient is prescribed medication from different groups (muscle relaxants, NSAIDs, analgesics, and so on). In some cases, neurological symptoms are observed, so a short course of sedation may be needed. In the early stages of the disease, physiotherapy and acupuncture are quite effective. It is considered mandatory to perform a set of special exercises that restore the mobility of the cervical vertebrae and strengthen the neck muscles. (See also: deforming arthrosis of the cervical spine).
Patients with cervical arthrosis should pay special attention to their lifestyle. First of all, posture deserves control when performing habitual actions: when working at a computer, while sleeping, and so on. Further, you will need to change the daily schedule so as to find time in it for periodic warm-ups, walks in the fresh air, sports and outdoor activities.
The main element of the treatment of cervical arthrosis and the prevention of various relapses is health-improving gymnastics. A complex of individual exercises must be prescribed by the attending physician, who at the same time takes into account the stage of the disease and the individual nature of its course, relying on various symptoms of neck arthrosis. Exercise should be done at a calm pace. In no case should sharp jerks be allowed, since any careless movement can aggravate the situation.
In any sports complex with cervical arthrosis should be included:
- tilting and rotating the head from right to left and back;
- throwing the head back and tilting it forward;
- circular movements of the head in different directions;
- raising and lowering the shoulders.
Each of these exercises is best done while sitting, since the specificity of the disease provokes dizziness. The time for performing a standard set of exercises to obtain a useful physical load is usually 10-15 minutes. Therefore, with sedentary work, it is quite possible to take a break every 1.5-2 hours to work on yourself a little. In addition, the regularity and frequency of exercise is important for the success of your recovery.
Also, in the fight against arthrosis of the cervical spine, manual therapy and massage sessions have proven themselves well. However, despite their benefits, these are also the most dangerous methods of exposure, so it is extremely important that they be carried out by an experienced specialist.
Prevention of cervical arthrosis
It is much easier to prevent the appearance and development of the disease than to deal with it and its manifestations later, and in the case of arthrosis of the cervical spine, there will be a lot of them. Therefore, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main, by the way, very simple preventive measures. The main preventative factor that reduces the risk of arthrosis is an active lifestyle, consisting of sports, daily walking at a brisk pace and morning exercises.
Another important point is a healthy diet. Proper nutrition excluding consumption a large number fatty and "empty" food, will provide the body with the necessary energy, and will not provoke the formation of extra pounds. By the way, a large weight in itself is a pathogenic factor, since it sharply increases the load on the joints, which occurs against the background of deteriorating blood circulation. As a result, you need to spend efforts to combat it and prevent the formation of fatty deposits.
Pay attention to the unique remedy for osteochondrosis, arthrosis and injuries!
Gel "Dedushkin Secret" is the first Russian drug that makes it possible to restore cartilaginous tissue in the joints without surgery and injections.
You can learn more about this tool by following the link below - Grandfather's Secret Cream.
mypozvonok.ru

- This is a state of deterioration or degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue and the bone adjacent to it, as a result of which pain is formed and appears. In the future, the disease leads to the formation of growths bone tissue, the so-called osteophytes or.Osteoarthritis of the spine most often affects people of middle age, as well as of retirement age, which is explained by the degeneration of intervertebral discs and articular tissue. If we consider the statistics of the disease in a global aspect, then up to 16% of the entire population of the world suffers from osteoarthritis. If at the age of up to 55 years, the disease often affects women, then after 60, almost every resident undergoes pathological changes in the spine.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the spine
The main symptoms of osteoarthritis of the spine include the following:
Emergence severe pain in that part of the back, the spine of which was subject to changes. Pain can occur in paroxysms. In the beginning, they are most often associated with physical activity, or arise after a long stay in the same position, sitting in an uncomfortable position. If you do a little warm-up, then the attack goes away. As the pathology begins to develop, pain becomes a constant companion, always pursues a person: during movement and during rest.
The joints are deformed.
With an exacerbation of the disease, the affected area becomes edematous.
If, due to deformation of the vertebrae, there is a clamping of blood vessels, then there is an insufficient blood supply to the brain, which leads to the occurrence and even.
General malaise.
Inability to perform the usual activities in full due to pain in the back and neck.
Crunching of the vertebrae when turning the body or neck.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the spine
The reasons leading to the development of osteoarthritis include the following factors:
Mechanical damage: injuries, excessive loads, both statistical and dynamic.
Overweight.
Anomalies in the development of the spinal column due to genetic characteristics.
Violation of blood supply, in particular: flying endarteritis, etc.
Disruptions in metabolism.
Acromealgia.
Many doctors studying the problem of the development of osteoarthritis of the spine agree that this disease is natural for every human body, as a result of its aging. Similar conclusions are made on the basis that after 40 years, the parts of the spine to one degree or another in the vast majority of people have undergone the destructive effect of osteoarthritis.
Diagnostics of the osteoarthritis of the spine
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will need to study the history of the development of the disease, interview the patient, and use palpation to establish the location of the pain and its intensity.
But on the basis of only physical methods, it can be quite difficult to make a diagnosis, therefore, to clarify the data, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
To establish the degree of damage to bone tissue, as well as disks and cartilage adjacent to it, an X-ray is assigned. But the disadvantage of this procedure is that it does not show the changes that occur at the initial stage, which means that early diagnosis of the disease is difficult.
To exclude such a pathology as rheumatism, which has similar symptoms, it is necessary to take blood for examination.
To detect damage to discs, as well as the presence of a narrowing of the lumens through which they exit spinal nerves, apply MRI.
An integrated approach to the study of the problem will make it possible to exclude the slightest mistake in the diagnosis, and therefore, to prescribe an adequate treatment for the disease.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl + EnterTreatment of osteoarthritis of the spine
Without timely therapy, osteoarthritis will continue to progress slowly and may ultimately lead to the person being unable to perform the simplest self-care actions due to pain.
If the disease is at an early stage, then doctors most often recommend wearing a support band, either the neck or the spine. Also, therapeutic massage, acupuncture courses, electrical stimulation of nerves through the surface of the skin are used as auxiliary methods aimed at improving blood circulation, relieving pain symptoms and accelerating tissue regeneration.
Perhaps the appointment of certain food additives as well as the use of heat compresses, ozonokerite and paraffin wax applications. Therapeutic baths have proven to be excellent: radon, hydrogen sulphide or simply based on sulfur. For the treatment of osteoarthritis, electrophoresis is performed with the following drugs: chymotrypsin, novocaine, sodium salicylate, analgin.
Shown a special therapeutic gymnastics, which includes a set of not too active exercises.
To reduce pain, it is advised to take analgesics and muscle relaxants. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hyaluronic acid derivatives can also be used successfully. Application of ointments and creams to the skin is often practiced. It will be useful to take vitamin complexes. It is imperative to properly equip the resting place. It is necessary to get rid of the old mattress, the new one must be firm, and the pillow must be chosen low.
Most often, the disease recedes, under the influence complex therapy... But if the MRI shows severe abnormalities or, despite treatment, osteoarthritis progresses, then surgery will be necessary. But it should be borne in mind that those nerve fibers that have already been damaged cannot be restored. Therefore, the earlier the treatment is started, the more effective it will be.
In the following conditions, it is necessary to consult a doctor for a diagnosis:
Neck or lower back pain.
Tingling or tenderness in the limbs.
Repeated occurrence or headache of unclear etiology.
Specialists to be visited for diagnosis are a neurologist, neuropathologist and orthopedist.
Author of the article: Kaplan Alexander Sergeevich, traumatologist, orthopedist