“Intervertebral hernia” - such a diagnosis is becoming more common and the reason for this is a sedentary way of life, only the treatment of this ailment prompts controversy and discussion.
What is an intervertebral hernia?
A herniated disc can occur after an injury or spinal injury. It can cause compression of the nerve structures.
The vertebrae are connected to each other by intervertebral discs in the spine. They have a high density and consist of an elastic core located in the center of the disc, the core is surrounded by strong rings, consisting of connective tissue. Numerous diseases of the spine are directly related to the destruction of the intervertebral discs.
Today, only a few indicators affect the appointment of an operational decision:
- does not go away within 6-7 months, is not removed by anything other than narcotic analgesics;
- progressive atrophy of the muscles of the limb, paralysis of the limb that does not go away;
- the functions of the pelvic organs are impaired;
- progressive spondylolisthesis.
Unspecified manifestations of such a hernia require only a conservative solution. With hernias, acute and prolonged pain can occur, which often prevents patients from objectively judging their condition.
predecessors intervertebral hernia- osteochondrosis in an advanced stage or injury spinal column. Depending on in which part of the spine the hernial protrusion is localized, the following symptoms occur: headaches, numbness of the upper or lower extremities, deterioration of mobility in the area of the affected disc. In some cases, paresis of the limbs occurs.
It is possible to treat a hernia of the intervertebral disc conservatively (using medications, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy) or surgically. Indications for surgery to remove a hernia: prolonged pain syndrome that is not amenable to conservative therapy, a large hernial protrusion that compresses the nerve endings and
Hernias can be localized in the thoracic, cervical or lumbar spine. Regardless of the location of the protrusion, doctors initially resort to gentle methods of therapy, and only when conservative methods have been tried, the neurologist will recommend surgery to remove the hernia. It is advisable to do the operation if the use of traditional methods of treatment for 1.5-2 months did not give positive results and the pain continues to torment the patient.
In addition to the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, the indication for surgery is the large size of the hernial protrusion. With a hernia of the thoracic or lumbar spine, surgery is necessary if the size of the protrusion exceeds 9 mm. The indication for immediate surgical intervention is the cauda equina syndrome, which is characterized by severe pain, change in tactile sensations, violation of reflex functions.
The size of the hernial protrusion in the thoracic and lumbar spine up to 5 mm is considered small, up to 8 mm - medium, above this size - these are large hernias, in which it is advisable to perform surgery.
With a hernial protrusion in the cervical region, the indication for surgery is a protrusion, the size of which exceeds 6 mm. A hernia of the intervertebral disc of the cervical spine is considered small with sizes up to 2 mm, medium - up to 4 mm, large - up to 6 mm, but even with this size, conservative therapy can be dispensed with. With a hernia over 6 mm, an operation is performed. Surgical intervention is also mandatory for spinal stenosis, even if the size of the protrusion is small or medium.
Preoperative diagnostics
As already mentioned, surgery on the spine should be done with intense pain, which cannot be removed by conventional therapeutic methods, with large hernial protrusions, with impaired sensitivity and motor activity of the limbs.
Before making a decision to conduct surgery, the doctor carefully examines the part of the spinal column in which the disc has ruptured with the release of the nucleus pulposus.
To determine the location and size of the hernia, magnetic resonance imaging is required. This method for examining the intervertebral disc is accurate and informative, but also complex. This method allows you to determine the size and localization of the hernial protrusion and identify concomitant pathological processes.
Also read:
Another study that is used for disc protrusion is computed tomography. However, this technique is not as effective as MRI (errors occur), and is less safe for the patient's body.
If, after treatment with traditional methods, the pain in the patient does not stop, dysfunction of the pelvic organs occurs, and the studies showed a large hernia, surgery is required. There are several methods for removing a pathological neoplasm.
Surgical intervention methods
Before performing an operation on a patient, one should carefully and deliberately approach the choice of a method for removing a hernial protrusion. Excision of a pathological neoplasm is performed in several ways, and all of them have their pros and cons. The choice of technique depends on the diagnosis, medical history and preferences of the patient. Not the last role is played by the financial condition of the patient. But most often, the pain makes the patient agree with the doctor, since the only desire of the patient is to get rid of the problem as soon as possible.
There are several ways to perform surgery for disc protrusion and hernial protrusion. This is:
- discectomy;
- microdiscectomy;
- laminectomy;
- endoscopy;
- nucleoplasty.
Each of these methods saves the patient from pathology. The pain subsides, and it seems to the person that tomorrow he can start vigorous activity. But after surgery, rehabilitation is necessary. In addition, it must be remembered that the removal of a hernia does not promise a 100% result, sometimes the pain returns, a relapse occurs.
Discectomy
This method is already outdated, it is necessary to do such an operation in extreme cases. The intervention takes place under general anesthesia - the surgeon makes a 10 cm incision and excised the affected disc. This is an inexpensive option for hernia removal, which requires antibiotic therapy and long-term rehabilitation. After the intervention, the operated person stays in the hospital for two weeks. Full rehabilitation takes place in three months.
The advantage of this method is the minimum percentage of relapses (3%).
microdiscectomy
This is a microsurgical intervention. Through a small incision (up to 4 cm), the surgeon using a powerful microscope, hernial protrusion and releases the compressed nerve root. After excision of the neoplasm, laser treatment is performed to regenerate damaged disc tissues.
After microsurgical excision has been performed, the patient is allowed to sit down, and rehabilitation in this case will take no more than a month. The patient is allowed to start vigorous activity with physical activity after three months of wearing a special supporting corset. The disadvantages of this method are relapses of up to 15% in the first postoperative year.
Endoscopy
This microsurgical intervention is performed using endoscopic instruments under epidural anesthesia. The surgeon controls his own actions through the monitor, since the instruments are equipped with a microscopic camera. The incision is made minimal (no more than 2 cm). This is a minimally invasive operation in which the muscles and ligaments remain intact. Already 1-2 days after hernia repair, the patient is allowed to go home, while rehabilitation lasts less than a month. This method has few drawbacks, so it is often used in surgery.
Cons: The recurrence rate is 10%, not all types of hernias can be removed by endoscopy, and this is an expensive operation.
Nucleoplasty
This minimally invasive procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Looks like this - in several places damaged disk small holes are made using a special needle. Laser or radio frequency radiation is transmitted through the hole of the needle, the gelatinous substance inside the disc is heated, under the influence of which it disintegrates, the pressure on the nerve roots subsides, and the pain syndrome disappears.
The operation is performed no more than an hour, a few hours after it the patient is allowed to go home, full rehabilitation lasts 1.5 months.
Laminectomy
Operation of the case under general anesthesia - the surgeon makes an incision up to 10 cm, through it a part of the vertebra is removed, to which the nerve process is pressed by a hernia. After the operation, rehabilitation in the hospital takes place for several days, the pain syndrome recedes immediately. Of the risks, the danger of infection and damage to nerve endings are distinguished.
After the operation, the recovery period is important, but this is not the time to lie on the couch. During this period, physiotherapy exercises are needed, it will help strengthen the muscular frame and reduce the risk of relapse.

Call the most acute manifestations of osteochondrosis of the spine. Most often, this disease is experienced by people in the age range of 30-60 years. In addition, it has been observed that men are more susceptible to it. We will try to figure out such a disease as a hernia on the spine, whether an operation is needed here and, if so, what type surgical treatment better to choose?
What types of operations to remove the intervertebral hernia will be offered to you?
There may be several types. The traditional method - discectomy - involves the removal of the disk with the further formation of a fixed connection of a pair of adjacent vertebrae.
Not so long ago, when removing a herniated disc, a laminectomy was often done. However, this method has some serious drawbacks: for example, a fairly large injury after surgical access.
The consequences of this injury became a source of problems during further recovery, when the hernia had already been removed. In particular, a long period of time was needed for the injuries to heal, as a result, the muscle of the damaged area noticeably weakened, which caused relapses.
That is why they began to develop methods that involve reducing the size of the surgical access and, consequently, the injury itself, as much as possible.
Are there more modern types of operations?
 The main significant change was the use of a surgical microscope. Thanks to him, the technique of intralaminar microsurgical removal of hernias arose; today it is considered, perhaps, the most optimal method in surgery.
The main significant change was the use of a surgical microscope. Thanks to him, the technique of intralaminar microsurgical removal of hernias arose; today it is considered, perhaps, the most optimal method in surgery.
Further, the operation to remove the intervertebral hernia began to be carried out using microsurgical, endoscopic and other methods. At the moment, surgical techniques for the treatment of hernia are developing along this path - the way to reduce the size of the injury during surgery.
Microsurgical operations are performed with special endoscopic instruments. Minimally invasive surgeries have several significant advantages when compared to conventional treatments. The traumatization of tissues during the operation is reduced, and in general the volume of surgical intervention, as well as the frequency of complications.
When using the endoscopic method, it is possible to significantly reduce the period of disability of the patient and their stay in the clinic.
Is laser hernia treatment effective?
 Minimally invasive surgical interventions during the treatment of intervertebral hernia include microdiscectomy, the use of B-Twin systems, as well as vaporization of the core of the affected area with a laser.
Minimally invasive surgical interventions during the treatment of intervertebral hernia include microdiscectomy, the use of B-Twin systems, as well as vaporization of the core of the affected area with a laser.
Intervertebral removal, despite advertising, cannot be attributed to some extraordinary methods. The use of lasers in this case acts more like a publicity stunt, which speaks of the advancement of medical technology.
In truth, the beams that are generated by the laser are very difficult to control, which means that there is a danger of damaging neighboring internal organs. In addition, the cost of laser surgery will be higher than when using other, not so "fashionable" methods.
How is an endoscopic microdiscectomy performed?
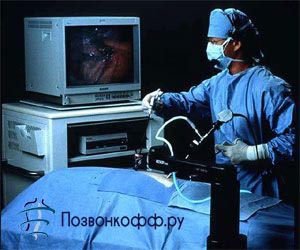 This operation is performed using local anesthesia. In the process, the endoscope (its diameter is 4 mm) is brought to the intervertebral disc of the hernia through a small incision (no more than 0.5 cm), all actions are projected on the screen of a special monitor.
This operation is performed using local anesthesia. In the process, the endoscope (its diameter is 4 mm) is brought to the intervertebral disc of the hernia through a small incision (no more than 0.5 cm), all actions are projected on the screen of a special monitor.
Under this visual control, a specialist removes both the hernia itself and the remnants of the nucleus pulposus of the disc with a special tool. It is worth noting that even a small part of the vertebra is not removed.
This operation is considered less traumatic when compared, for example, with traditional microdiscectomy. This reduces the risk of complications and reduces the postoperative period of rehabilitation. In many cases, the operation is completed with a restorative treatment of the operated site with lasers.
An extract from the clinic is made, if not on the very day of the operation, then after 1-3 days with the opportunity to engage in non-physical activities almost the next day after being discharged, and after 2-6 weeks - to physical labor.
How is the operation "destruction of the facet nerves"?
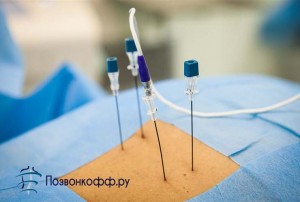 An operation to remove a herniated disc is possible in the form of destruction of the facet nerves. In other words, this is a minimally invasive surgical intervention, which consists in inactivating pain receptors in the intervertebral joints (the second name is facet joints).
An operation to remove a herniated disc is possible in the form of destruction of the facet nerves. In other words, this is a minimally invasive surgical intervention, which consists in inactivating pain receptors in the intervertebral joints (the second name is facet joints).
This procedure will be more effective if there is a so-called "facet syndrome" - this pain syndrome that occurs during arthrosis of the intervertebral joints.
To confirm this diagnosis, you first need to conduct a special blockade of these nerves. Only in the case of positive dynamics of nerve blocking, it is possible to perform radiofrequency destruction of the facet nerves using a radiofrequency probe, which is brought to the nerve by puncture. This procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, it lasts half an hour (the exposure to radio frequencies itself is 2 minutes), most often patients tolerate it quite easily, after an hour the patient can go home.
Want to learn more about laser vaporization?
 It has completely different reviews on the Internet. What does she represent? Laser vaporization is the irradiation of the intervertebral disc with a special laser beam in a destructive mode. Such irradiation does destroy part of the disc: evaporation occurs, which reduces the pressure inside the disc by up to 30% and therefore reduces disc herniation.
It has completely different reviews on the Internet. What does she represent? Laser vaporization is the irradiation of the intervertebral disc with a special laser beam in a destructive mode. Such irradiation does destroy part of the disc: evaporation occurs, which reduces the pressure inside the disc by up to 30% and therefore reduces disc herniation.
This technique is often used for patients in the age range of 20-50 years, at an early stage of damage to the intervertebral disc. Recall that at an early stage, the protrusion of the fibrous ring does not exceed 6 mm. For older patients and in the presence of severe degenerative disc changes, this method is not always suitable.
At the same time, such an operation can not only therapeutic effect but also preventive. This is because the disc that has been vaporized due to fibrosis and sclerosis developing on it then does not move, which means that the risk of hernia progression is noticeably reduced.
This procedure for getting rid of a hernia will take about one to two hours in a hospital, the operation itself will last from 20 minutes to half an hour.
How is laser disc reconstruction performed?
 This type of intervertebral disc surgery involves irradiating the intervertebral disc with a special laser beam in a non-destructive mode. With such irradiation, the disc is heated, and this stimulates the growth of cartilage cells and restores the patient's intervertebral disc. New cartilage cells in the period from 3 months to six months fill the cracks in the disc, which causes the absolute disappearance of acute and even chronic pain in the patient's spine.
This type of intervertebral disc surgery involves irradiating the intervertebral disc with a special laser beam in a non-destructive mode. With such irradiation, the disc is heated, and this stimulates the growth of cartilage cells and restores the patient's intervertebral disc. New cartilage cells in the period from 3 months to six months fill the cracks in the disc, which causes the absolute disappearance of acute and even chronic pain in the patient's spine.
This irradiation procedure takes place in the form of a needle puncture of the affected area of the body. The entire treatment process will take from two to three days in the hospital. This procedure can be performed both independently and when the patient has a hernia removed in order to prevent its recurrence.
Is surgery necessary for a cervical hernia?
 If the hernia on the neck is in an advanced stage, then you should resort to surgical intervention. The purpose of such an operation is to decompress not only spinal cord but also the root of the spinal cord.
If the hernia on the neck is in an advanced stage, then you should resort to surgical intervention. The purpose of such an operation is to decompress not only spinal cord but also the root of the spinal cord.
In the process of removing the cervical disc, it is necessary to stabilize the diseased segment. For this, various special implants are used, and, in addition, prosthetics of the intervertebral disc.

The information on the site is provided for informational purposes only, does not claim to be reference and medical accuracy, is not a guide to action.
In no case do not self-medicate. Consult with your doctor!
Tell your friends.
In some cases, osteochondrosis develops into a herniated disc, which is an exacerbation of the disease. As a rule, patients whose age is 30-60 years old are susceptible to this disease. Mostly men suffer from the disease.
Surgery to remove a hernia of the spine is not necessary in all cases. Before deciding on it, it is necessary to use all possible methods of conservative treatment. If they do not give a result, and the pain becomes stronger, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
The operation is assigned in the following cases:
- With relative indications. Assigned if conservative treatment ineffective.
- For absolute readings. The hernia interferes with the functioning internal organs, men complain about the lack of erection, the work of the pelvis is disturbed, there are failures in cardiac activity.
Depending on the type of indication, a certain technique and surgical intervention is prescribed.
Radical operation
In this case, along with a hernia, a pathologically altered disc is subject to removal. Instead, an implant made of titanium is installed. It is able to repeat the atomic structure of a spinal segment. This type surgical intervention is used not only at the stage of development of the disease, but also with a sequestered hernia.
The disadvantage of this method is that sometimes it can be found that the pain was not caused by a hernia, but by another disease that can be easily eliminated without surgery. In addition, some patients report that their well-being has not improved after surgery. Thus, if there are no absolute indications, it is better to use conservative therapy.
Minimally invasive surgery
This method involves the use of a laser. The light guide is inserted into the intervertebral disc and heats the elements of the nucleus. This results in the evaporation of water. The nucleus of the disc decreases in size, the hernia protrudes less. Such an operation is prescribed at the stage of a true hernia of the spine.
This method is non-traumatic. It practically does not violate the structure of the spine, has a minimal rehabilitation period (up to a month) and does not require a long stay in the hospital.
Endoscopic microdiscectomy
Surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia. In this case, the endoscope is inserted through a small incision and reaches the intervertebral disc.

The actions taken are displayed on the monitor. The doctor removes the cause of the disease with a special tool.
The advantage of the method is that no vertebra is touched. The patient is discharged from the hospital the next day after the operation or three days later. This method of hernia removal is considered the most optimal, it is used in medical practice quite often.
Laser reconstruction of discs
It is irradiated with a laser. The disk heats up, which stimulates the growth of cartilage cells. They fill in the cracks. As a result, the disk is restored, pain disappears. The rehabilitation period takes approximately three months to six months.
Destruction of the intervertebral nerves
The technique provides for the relief of pain in the patient. First of all, there is a blocking of the receptors of the intervertebral space. For this, an anesthetic is used. The surgeon can then determine the cause of the pain, which may or may not be a hernia. In this case, the operation is excluded. The technique of destruction of nerves is used.
This method of treatment allows you to quickly restore performance, relieve pain, does not require long-term rehabilitation. Negative effects are adhesions and scars that form in the intervertebral canal, nerve injuries due to changes in the functioning of the pelvis, subsidence of the vertebrae, inflammatory and infectious processes.

Possible consequences
The most common complication after surgery is hernia recurrence. It is possible not only in the early stages of rehabilitation, but also at a later date. The return of the disease usually occurs due to a violation of the recovery regimen. For example, the patient returned to the previous physical activity too early.
It is also possible to develop inflammatory process at the sites of surgical intervention. In order to avoid it, antibiotics are prescribed. Often a complication delivers an intense scarring process, as a result of which the nerve roots of the spinal cord are pinched.
Recovery period
When the operation to remove the hernia of the spine is performed, the patient will need some time for rehabilitation. At this stage, restoration activities are carried out. They consist in the need to wear a special corset. It is also recommended to avoid excessive physical exertion, sudden movements, so that the hernia does not reappear. In the process of surgical intervention, mechanical damage is applied to the patient's body.
To heal wounds faster, it is necessary to limit movement to a minimum. In addition, you need to listen to your feelings. When you first get out of bed, you need to make sure that there are no dizziness. The stitches are usually removed on the tenth day. It is recommended to sleep on a hard mattress.
Thanks to the development of medicine, today there are many ways to treat this disease. Before making a choice, a mandatory consultation with a specialist is required.
