/ Deforming grade 2 treatment
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
What is osteoarthritis of the hip?
Osteoarthritis hip joint - This is a destructive process that is localized in the joint, cartilage plastics, which are its inner coating, suffer from pathology. Among all joint diseases, it is osteoarthritis of the hip joint that is the most common. This pathology accounts for up to 40% of all cases. People have been suffering from osteoarthritis of the hip joint for many millennia. This fact is confirmed by the bones found during the excavations, which have the corresponding signs of the disease.
If the source is lumbosacro-radicular, the active movement of the hip in flexion does not reproduce the patient's pain. Since both sources of pain can coexist, it is important to determine which one is the predominant complaint. A thorough neurologic examination combined with electromyography will help.
Vertebral bursitis is another cause of pain in the hip joint. This patient complains of lateral hip pain but has good passive range of motion. Unlike pain that actually arises from the hip, tenderness is localized over the greater trochanter on the lateral aspect of the leg and not in the groin. In this case, administration of the bursa with lidocaine and corticosteroid often gives excellent relief.
These include the following:
The nature of the destruction of cartilaginous tissue is degenerative - dystrophic in nature.
Bone tissue grows along the edges of the joint.
The joints themselves undergo significant deformations.
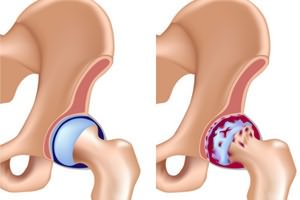
The essence of the disease is as follows: inside the joints located at the end of the bones there is cartilage, due to which normal limb mobility is ensured. It allows bones to slide without unnecessary friction. But over time, the cartilage begins to retain the fluid necessary to ensure movement, and in the process of "exploitation" it begins to crack. The bones begin to rub against each other, certain growths, called osteophytes, form on them. Because of them, a person experiences painful sensations and other symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
Before starting therapy, the physician should conduct a complete assessment, including medical history, medical history, and physical examination. Many osteoarthritis patients are elderly, have underlying medical conditions, and are taking medications that may interact with patients prescribed for osteoarthritis. In addition, when a physician makes a full assessment, other conditions that can cause joint pain can be identified and treated.
Too often, patients who are diagnosed with arthritis see themselves in a wheelchair. The first duty of a physician after diagnosis is education. A simple discussion of the prognosis is always helpful and the patient should encourage the clinician to provide it. Disease-specific brochures are available from the local chapter of the Arthritis Foundation.
The risk of getting this pathology increases in people who have crossed the age limit of 45 years. The female sex is more susceptible to osteoarthritis than men. This is due to the changes occurring in her body during menopause, when the calcium so necessary for the bones begins to leave them against the background of hormonal transformations. It accumulates in large quantities in cartilage and destroys them. But women do not always suffer more often than men, at a young age representatives of the strong half of humanity suffer more from the disease.
Physical and occupational therapy includes exercise and physical conditions. Exercise, including controlled fitness walking, maintains the range of motion and integrity of the supporting muscles. The patient lies on their back with the affected leg straight and the ankle is dorsiflexed to 90 °, then pulls the quads by pressing the back of the knee onto the bed and holding it for ten seconds. This maneuver is repeated ten times, twice a day.
In addition, the patient, lying on their back, lifts the affected leg ten inches from the bed and holds this position for ten seconds, also repeating this maneuver ten times twice a day. Swimming, where one hit from the hips with a straight leg is another form of strengthening the quads. Exercise that causes pain in the affected joint should be stopped. Although weight loss has only proven beneficial for osteoarthritis of the knee in women, a weight loss program is essential for the overall overall health of overweight patients.
Degree of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Depending on how much the disease has progressed, it can manifest itself with the following symptoms in varying degrees of severity:
Pain in the thigh area of varying intensity. They can occur both with increased physical activity and during rest.
There is no specific diet that is effective in treating arthritis. Acupuncture is based on naturalistic theories that are compatible with Confucianism and Taoism, and its use for pain relief is increasing with the number of doctors trained in their practice. There are some uncontrolled trials in osteoarthritis of the knee and low back pain showing benefits.
These guidelines were derived from data that demonstrated that the first non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs available, which are nonspecific cyclooxygenase inhibitors, are costly in terms of side effects and do not have a higher benefit than that provided by acetaminophen. Professor John Wayne received the Nobel Prize for elucidating the mechanism of action of aspirin. Side effects associated with the gastrointestinal, renal, and hematopoietic systems have limited their usefulness.
There may be some stiffness of movements, their limitation.
While walking, a sick person limps, a wide step becomes inaccessible to him.
With the progression of the disease, there is a shortening of one leg relative to the other. The affected limb becomes shorter.
If left untreated, osteoarthritis will eventually lead to atrophy of the thigh muscles.
The mechanism of the pathological process
A second system of cyclooxygenase enzymes has been described. In this cohort, after 18 months of taking the drug, there were 50% more cardiovascular events than in the placebo group. In another subgroup analysis, the relative risk was the same regardless of whether patients were taking concomitant aspirin. Although the number of patients involved was small compared to those who received treatment and occurred after 18 months of treatment, the company still felt it necessary to take the drug off the market. Refers to the relevance of this issue and gives us some recommendations that should be followed.
At the first stage, the diagnosis of the disease is significantly difficult due to a number of factors:
Firstly, the symptomatology of the disease is not clearly manifested, which makes it possible to confuse the disease with a number of others, or even to associate recurrent pains with other causes that are not related to any pathology.
Secondly, the patients themselves are in no hurry to see a doctor.
However, not all patients benefit from these drugs and some develop side effects including nausea, diarrhea, and swelling. Whether they affect kidney function in normal patients is still unknown. Corticosteroids, both parental and oral, do not play any role in the treatment of osteoarthritis. However, an injection with intra-articular steroids for a particularly painful joint sometimes helps. These drugs should be combined with 1 cc of lidocaine in large joints such as the knee, shoulder, and ankle.
Do not enter any compound more than four times a year. Each injection should result in at least three months of relief. Pain relief lasting less than 2–3 months should be considered a failure and not repeated. In normal joints synovial fluid changes from viscous to elastic with increasing load, providing a friction-free surface. Enzymes and free radicals generated during inflammation in osteoarthritis degrade hyaluronic acid, leading to its loss of viscous and elastic properties.
Nevertheless, X-ray examination already at this stage makes it possible to see some changes in the joints. Small bony growths are noticeable, but they are located within the bony lip. Localization of growths - along the outer and inner edges of the acetabulum surface. At this stage, the disease has not affected the femoral neck and head of the bone, no visible changes are found.
Degraded hyaluronic acid itself contributes to joint damage. Two drugs have been approved for the treatment of osteoarthritis knee joint... One drug, isolated from rooster combs, requires five weeks of injections, while another product with a higher molecular weight obtained by crosslinking hyaluronic acid molecules with formaldehyde and vinyl sulfone, requires three weeks of injections. Tidal lavage of the osteoarthritic joint with saline failed the clinical time test.
Both publications claimed that these agents treat the symptoms of osteoarthritis and slow down structural damage. After three years, patients on glucosamines not only had clinical improvement, but also had less progression on their chest radiographs. This represents the first well-controlled study on this subject. The National Institutes of Health's Office of Alternative Medicine has initiated a large placebo-controlled trial of glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and their combination.
As symptoms inherent in this stage of the development of the disease, the following can be distinguished:
Decreased motor activity due to recurrent pain.
Pain that occurs with increased physical activity. In a state of immobilization, a person is not disturbed by any manifestations.
Occasionally, slight clicks can be heard while moving the hip.
Pending the completion of this test as it is nutritional supplements They can be sold without approval from any government agency without security standards. When faced with the question: Should you use glucosamine or chondroitin sulfate, what should be the answer? Or “Does my aunt say it works for her?” I advise my patients that I can and should inform them of methods that have been scientifically proven and safe.
These reactions are important both for the generation of cytokines that affect the function of synovial cells and for reactions associated with proteoglycan synthesis. While some animal studies are encouraging showing improvements in cartilage histology, a few short-term clinical studies have not demonstrated any superiority over standard drug therapy. The future: experimental therapy.
When making sharp swings with a limb, sharp pain may occur.
At the same time, a person's movements are practically unlimited, the gait pattern is not changed, his muscle strength remains normal.
Diagnosis of second-degree hip osteoarthritis is not so difficult. Most often, patients already independently come to the doctor's office with complaints of painful sensations. They arise when a limb moves, even when walking. On palpation of the affected limb, the patient feels pain.
The applied methods of treatment
Unlike rheumatoid arthritis The development of agents that will not only reduce symptoms but also prevent further deterioration in osteoarthritis has suffered from methodological problems - the least of which is the long time it takes for the disease to manifest.
A potential long-term cure or treatment for osteoarthritis is the development of agents that alter the balance between the degrading and synthetic processes of the chondrocyte. In animal studies, doxycycline inhibits cartilage collagenase activity and reduces the severity of osteoarthritis. Transforming growth factor beta, packaged in liposomes, can repair partial damage to articular cartilage in animal models. Many pharmaceutical companies are testing pharmacological inhibitors of cartilage matrix degradation enzymes and cytokine blockers.
An X-ray image reveals conditions such as: narrowing of the joint space, by about 45%, the synovial cartilage is already damaged, which causes the bones to rub against each other, and therefore pain. But to a greater extent, it manifests itself due to the occurrence of puffiness, which appears against the background of malfunctioning of the joint.
Osteophytes are clearly visible in the picture, they significantly aggravate the course of the disease and negatively affect the general condition of a person suffering from osteoarthritis of the hip joint. Sometimes the image can show the so-called "articular mouse" - as doctors call a splinter that has moved away from the bone and is inside.
The causes of the disease
This function is decoupled from their antimicrobial activity. A national multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study is currently underway investigating disease or structural modification in obese women with knee osteoarthritis.
Although this procedure can be applied to young people with traumatic injuries less than 3 cm, for whom the goal is to prevent secondary osteoarthritis, this procedure does not rejuvenate end-stage osteoarthritis knee. Gene therapy is another strategy in which non-replicating viral vectors can deliver genes that have either anti-arthritic or synthetic properties for synovial and articular cartilage.
The main symptoms are the following:
Pain is present all the time, and not only when a person is in motion. It can radiate to the groin area, as well as to the knee joint.
The patient gets tired quickly, it is difficult for him to be in a standing position for a long time, and even more so to perform any active actions.
When conservative treatment for osteoarthritis fails, and when pain in a particular joint disables the active person, targeted surgery can restore the patient to normal activity. The general practitioner is expected to ask his patient about the correct procedure and the correct timing of these interventions. Surgery relieves pain more than it restores range of motion. Thus, the decision to work is another personal rather than a medical priority. The best candidate for surgery is a patient who has a certain interruption in some kind of daily life, as well as unsuccessful physical and pharmacological therapy.
Movement is largely limited, the joint is stiff.
The pain does not appear in the process, but at the very beginning of the action of the affected limb.
The articular surface is deformed.
The range of movements, although somewhat limited, nevertheless, a person is able to perform all self-service actions. Sometimes, already at this stage, the patient begins to use the cane. At least - this is a doctor's recommendation and greatly simplifies the patient's life.
For this patient, the result will be outstanding because it will be painless in the involved joint. For osteoarthritis of the hip and knee joints, general joint replacement is the preferred therapy for patients over fifty years of age. The decision between a cemented or non-cemented prosthesis is technical, which revolves around the patient's age, the condition of the joint, and the experience of the surgeon. With each revision, there is less bone material and the procedure is more complicated. The reason is that many surgeons suggest that younger patients undergo hip and knee osteotomies in front of the common articular artery.
The third degree of osteoarthritis of the hip joint is very easy to diagnose, but it should be said that this is a rather late date for detecting the problem. X-ray examination shows that the joint space has almost completely disappeared.
Symptoms typical for this stage are as follows:
Constant, unremitting pain.
Pronounced joint crunch during movement.
Palpation is incredibly painful.
The joint is significantly deformed.
Movements are almost impossible, and if untreated, they will be completely lost.
The patient is able to move only with support on a cane.
On this topic: Hip pain
Deforming osteoarthritis is chronic illness that slowly recurs. It results in persistent disorders in the activity of the joint. If we consider all bone diseases associated with degenerative - dystrophic changes in bones and cartilage, then it is deforming osteoarthritis that takes the leading position. This is largely due to the fact that it is the hip joint that experiences the most severe stress and is the largest in the human body.
The process proceeds as follows: hyaline cartilage begins to deplete, irregularities and roughness can be found on it. Then the disease leads to the fact that he completely disappears, exposing the bone tissue. During movement of the limb, the bones rub against each other, since there is no natural shock absorber between them. Within a short period of time, this leads to the fact that the joint loses its function and is significantly deformed.
There are two types of deforming hip osteoarthritis: one that occurs against the background of a functional load and affects an absolutely healthy joint (called primary osteoarthritis) and one that arises as a result of an existing disease (called secondary osteoarthritis).
The factors influencing the occurrence of this pathology include the following:
Overt and hidden injuries of the hip joint.
Age over 45.
Hereditary predisposition.
Hormonal disruptions in the body, as well as disruption of normal metabolism.
Excess weight.
Congenital dislocation of the hip and hip dysplasia.
Peters' disease.
The disease can destroy one or both joints.
Treatment requires, if not complete, then the maximum possible rest for the injured limb. It is also required to eliminate the main symptoms of pathology: to alleviate or completely eliminate pain, and also to return the person's freedom of movement. Hospitalization for the treatment of osteoarthritis is most often not required.
The therapeutic scheme is selected individually, taking into account age characteristics the patient, as well as the stage of development of the disease:
Anti-inflammatory drugs. To relieve painful sensations, a person is prescribed the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or standard analgesics. Hormonal agents that are injected into the affected joint may be recommended. For this purpose, Kenalog or Dexazon is used, which greatly facilitates the patient's condition, gives him the opportunity to move freely.
On this topic: List of modern medicines and drugs for joints
Chondroprotectors. Chondroprotectors can be prescribed, for example Teraflex and Aflutop, it is they who contribute to the fact that the cartilage tissue begins to regenerate on its own.
On this topic: Modern dietary supplements for the restoration of joints
Physiotherapy. After the mobility of the joint is somewhat restored, and the pain is relieved, doctors prescribe a course of physiotherapy procedures. They are great at reducing inflammation. For treatment, a specialized set of exercises is prescribed, and electrophoresis is possible. A visit to a massage parlor and laser therapy give good results. After the inflammation has been relieved, most doctors recommend that patients go to the pool. It is the water procedures that will help to strengthen the muscles and tissues and will more reliably fix the diseased joint.
Surgery. As for surgical intervention, it is usually used at 3 stages of the development of the disease, when the process of the joint is steadily deformed, and the person is not able to perform normal movements. Surgical intervention is called endoprosthetics and consists in replacing the diseased joint with an artificial one. After it is carried out, a person will be able to move independently and will not be limited to bed rest.
Diet. It is also necessary to combine medical procedures with a specific diet recommended by the doctor. Its principle is that a person should stop consuming meat, fatty and sweet foods. You should not completely exclude meat from the diet, but you should limit yourself to the consumption of lean beef and chicken. It is important to eat fish, fruits and vegetables, and brown bread.
To reduce the load on the sore joint, especially during treatment, it is important to use a cane.
On this topic: Effective home remedies
A method of stretching the damaged joint is also practiced. Such manipulations can only be carried out in a hospital, in inpatient treatment. Patients can move during the course of the course only with the use of crutches, so that the load on the injured leg is minimized. When combined with a massage performed by a professional, the results will surpass all expectations. After completing the course and returning the patient home, it is necessary to continue to exercise therapeutic actions on one's own. To consolidate the result, you need to exercise, massage the sore limb and attend specialized classes in the pool.
It should be understood that osteoarthritis of the hip joint, thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, is perfectly treated. But it is important to start therapy on time. If time is lost and the doctor recommends an operation, then you should not refuse it. Surgery gives excellent results and allows patients to live an active life without discomfort in movement.
Author of the article: Kaplan Alexander Sergeevich, traumatologist, orthopedist
ayzdorov.ru
How to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint
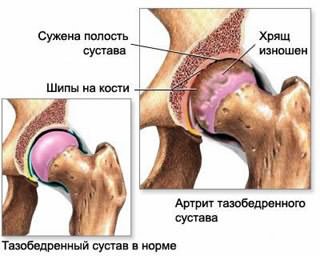
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a degenerative disease that causes pain and inflammation in one or more joints. The disease can cause disability in older people.
The structure of the hip joints
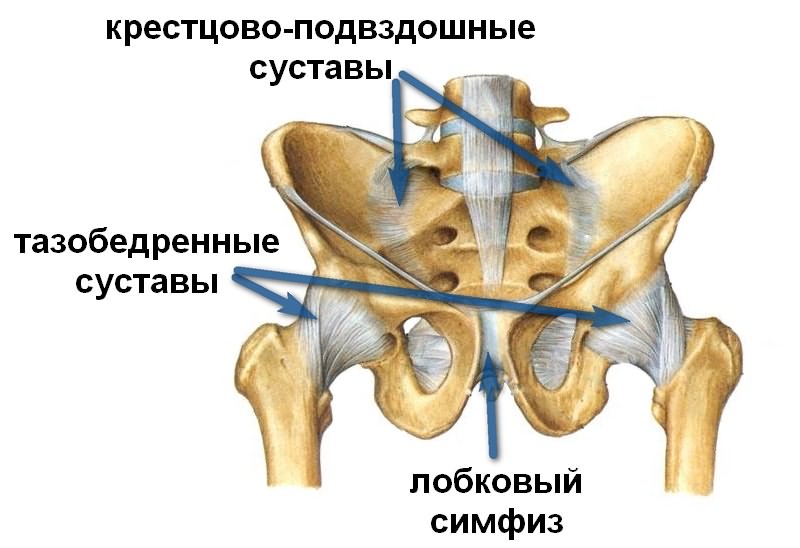
The hip joint connects the ilium and femur. It is similar to a hinge, so a healthy person can make various movements. Articular cartilage lines the surfaces of the bones of this joint, so that they can easily slide relative to each other.
In order for the hip joint to perform its functions, it is surrounded by powerful muscles. They take on significant loads, acting as a shock absorber and providing movement of the body. Muscles help pump blood into circulatory system, ensuring a complete supply of nutrients to the hip joint.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint causes a chronic inflammatory process in the joint. The body does not produce enough articular fluid, so the amortization of the cartilage decreases, and the wear of the bones increases. They rub against each other, causing pain, bone destruction.
If adequate treatment is not provided, over time, the cartilage is completely erased, and the hip joint ceases to function. At the same time, it is lost muscle tone, which accelerates the process of bone deformation.
Causes of development and symptoms of the disease
Symptoms are often slow onset and worsen over time.
- Pain during or after movement.
- Stiffness in joints. Most noticeable when the patient wakes up in the morning or after a period of inactivity.
- Loss of flexibility in the joints.
To clarify the diagnosis, a blood test is performed, its results help to exclude other ailments. The manifestations of this joint pathology of the 1st degree cannot be detected with the help of an X-ray examination. Cartilage is not reflected on conventional x-rays. This explains the late diagnosis of such diseases. Only at the stage of sufficiently serious destruction of bones does it become possible to recognize osteoarthritis of the hip joint. A clearer picture of the state of the joint is given by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. These diagnostic tools can detect early development illness.
Nowadays, the question of a complete cure for this ailment is not worth it. Medications do not affect the root cause of the onset of the disease. But proper treatment of osteoarthritis can significantly reduce pain and maintain joint mobility.
Conservative treatment methods
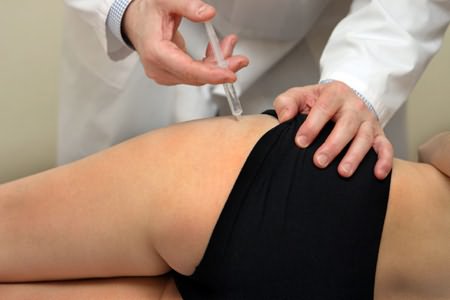
- The first step in treating an illness is pain relief. This can be done with the combination medicines, exercise and physiotherapy. Pain relievers can help relieve pain, but not inflammation. In addition, high doses of paracetamol can damage the liver. The use of analgesics will lead to an increase in blood pressure, deterioration of kidney function, gastric ulcer and cardiovascular disease.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Stronger non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are available with a doctor's prescription. NSAIDs have side effects. They can cause upset stomach, ringing in the ears, heart and vascular problems, bleeding, liver and kidney damage.
- Chondroitin and glucosamine have been shown to be effective in osteoarthritis. They can slow down or prevent further joint damage.
Surgical intervention
If conservative methods treatments do not help, the doctor may suggest other effective procedures.
Sports will help cope with illness
Lifestyle changes and home treatments can help reduce symptoms. If a patient has osteoarthritis of the hip joints, this does not mean that an active lifestyle is not available to him.

Helper methods
- It is good to lose weight. Since being overweight puts more stress on the weight-bearing joints, even a little weight loss can reduce pressure on sore bones and reduce pain.
- Your doctor may recommend using special insoles for your shoes, as they can help reduce pain when standing or walking by relieving stress on a sore joint.
- Use assistive devices that can make walking painless and easy. The cane will relieve the joints and muscles of the hip as you walk.
- Acupuncture. Some studies show that this therapy can relieve pain and improve hip function. During acupuncture, the finest needles are inserted into special acupuncture points on the body. Potential risks are associated with infection, bruising, and some pain where the needles are applied.
- Use heat and cold to manage pain. Heat relieves stiffness, and cold can relieve muscle spasms and pain.
- The use of special anesthetic creams helps. Such agents can provide temporary pain relief from hip joint disorders. Some drugs numb the pain by creating a feeling of warmth or coldness.
It is necessary to use all means that will help relieve the joints and muscles of the thigh. Osteoarthritis can be successfully treated. This will improve the quality of life.
MoiSustav.ru
How is osteoarthritis of the hip joint treated?
Without proper treatment, the disease is fraught with a fracture of the femoral neck, disability, or a complex hip replacement surgery. Since it is very difficult to stop the destruction of cartilage tissue, treatment must begin with the first symptoms.
How does it happen and who is susceptible to the disease?
Within the joints, the endings of the bones contain elastic cartilage, which allows the bones to slide in the joint without friction. However, as a person ages, cartilage tissue is less able to retain water and cracks. And without cartilage (a slippery and smooth shock absorber), the bones cling to each other, and at their edges peculiar spines, called osteophytes, are formed, which impede the movement of a person. This is how osteoarthritis of the hip joint develops.
osteoarthritis
Most often, people after 45 years of age are susceptible to the disease. At the same time, women suffer significantly more than men. This is due to the fact that after menopause in women there is a "leaching" of calcium (Ca) from the bones and its accumulation in the cartilage, which causes the development of the disease.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the disease is osteoarthritis of the hip joint, the symptoms are practically absent. And for several years a person may only have a feeling of stiffness in the joints after sleep.
But the development of the disease, its progression bring the patient a feeling of pain in the groin, which often spreads to the thighs, and to the buttocks, and to the lower leg or knee.
The late stage of osteoarthritis of the hip joint is characterized by the presence of severe pain and limited mobility, which affects the deterioration of the patient's quality of life and can lead to disability.
symptoms of osteoarthritis
Consequences of the disease
At a late stage of the development of the disease, when the restoration of cartilage tissue is impossible, the only alternative to possible disability is hip replacement surgery, which is distinguished by its complexity during execution.
But many patients note that one of the most unpleasant complications of osteoarthritis is a hip fracture, the treatment of which takes a long time and is difficult. This is due to the fact that the cartilage eventually loses its shock-absorbing properties and, accordingly, when walking, the load on the thigh bones increases.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joints should be started at the asymptomatic stage of the disease. People at risk of the disease, especially women over 45 years old, should be examined by a specialist annually, because at an early stage, the disease can be detected with the help of special studies.
How to prevent the disease?
The slowdown in the development of osteoarthritis is facilitated by an increase in the diet of a sick person in the proportion of fish and fruits, vegetables and black bread, dairy products and lean meat. It is not superfluous to refuse butter, by-products, lard, and also sausages.
In addition, a large amount of onion and garlic should be present in the patient's diet - food rich in sulfur, a trace element necessary for building cartilage tissue.
physical exercise
Also, in case of illness, it is better not to use black pepper, egg yolk, tomatoes and potatoes. These foods contain solanine, which can increase pain in osteoarthritis.
Pain during movement in advanced stages of the disease can be reduced by using a cane. It reduces the load on the hip joint affected by osteoarthritis by half.
An important role in the treatment of osteoarthritis is played by classes physical exercise to a moderate extent. For example, cycling and swimming are ideal.
The degree of the disease
There are three degrees of osteoarthritis disease:
Grade 1 osteoarthritis of the hip joint is characterized by recurrent pain sensations, which are mainly manifested after physical exertion (for example, prolonged walking or running).
Localization of pain is in the area of the affected joint, but sometimes extends to the hip and knee joint. After rest, the pain subsides. In this case, the range of motion is not limited, the gait pattern does not change, as does muscle strength.
As a result of X-ray examination, small bony growths are revealed that do not go beyond the articular lip. They are located along the outer and inner edges of the articular surface of the acetabulum. In this case, the femoral neck and head practically do not change.
With osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree, the pain syndrome increases and is more intense. In addition to pain in the joint, it spreads to the groin and thigh. Pain syndrome manifests itself even when the patient is resting.
Prolonged walking and exercise cause lameness. The joint can no longer function normally. The range of motion is significantly limited, and the muscles that are responsible for hip abduction and extension are weakened.
X-ray results show bony growths located along the outer and inner edges of the acetabulum and extending beyond the cartilaginous lip. The femoral head undergoes deformation and increases in size, acquires an uneven contour.
The appearance of cysts in the loaded parts of the acetabulum and head is possible. The femoral neck thickens and expands. Upward displacement of the head of the hip bone is possible.
Osteoarthritis grade 3 is characterized by the presence of constant pain that does not stop even at night. They have a sharp restriction of movement in the joint, and the muscles of the buttocks, lower legs and thighs atrophy.
There is a shortening of the affected limb, because due to the weak abductor muscles of the thigh, the pelvis tilts in the frontal surface. The patient, in order to reach the floor while walking, steps on the toes and tilts the body to the affected side. Thus, it compensates for pelvic tilt and limb shortening. However, this method leads to a shift in the center of gravity and overloads on the joint.
Radiographic findings show extensive bony growths on both the femoral head and the acetabulum roof. The femoral neck expands significantly.
Osteoarthritis treatment
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint of the first two degrees is treated on an outpatient basis. In this case, therapy has the following goals:
- decrease pain;
- reduce the inflammatory process in the damaged joint;
- improve blood circulation and metabolism in it;
- normalize mobility.
Reducing the severity of pain is facilitated by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or analgesics. But it should be remembered that in old age they have a bad effect on cardiovascular system and the gastrointestinal tract. Biostimulants and vitamins contribute to the improvement of the metabolic process in tissues.
Drugs called chondroprotectors are widely used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, the composition of which is full of various components of cartilage tissue of animal origin. So chondroprotectors contain chondroitin sulfate, which helps the cartilage retain water. Chondroprotectors help to reduce pain and stiffness of the joints, slow down the progression of the disease.
Chondroprotectors
The use of pain-relieving compresses is shown. A highly effective compress based on Dimexide is applied to the affected area of the hip joint. The duration of the course is 12-15 procedures.
How to treat grade 3 osteoarthritis of the hip joint? As well as the first two degrees, however, in this case, doctors also recommend an additional course of physiotherapy. For example, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, etc.
After improving mobility and reducing pain, you can take a course of massage in the hip, hip joint, buttocks and attend physical therapy classes. This improves muscle tone, strengthens the muscles around the hip joint, which improves its mobility.
In some cases of the disease, doctors recommend traction of the affected joint, which is performed on the basis of an inpatient facility. During this period, the patient is recommended to move with crutches in order to unload the affected hip joint as much as possible. Also, in combination with traction, a course of classical or underwater massage is usually prescribed.
At home, after the end of the main course of therapy, the patient is recommended to use additional procedures. In order to consolidate the achieved result, swimming, self-massage of the muscles of the buttocks and thighs, and physical therapy are ideal. However, one should seriously approach the choice of exercises, since patients with osteoarthritis should not heavily load the lower extremities.
Treatment with traditional medicine methods
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joints using traditional medicine is quite effective.
Honey-based recipe. We take 1 tbsp. a spoonful of natural honey, vegetable oil and mustard, mix and pour into an enamel bowl. Bring the mixture to a boil, cool and filter. We use the broth as a compress on the affected area. We keep the compress for about 2 hours and repeat the next day.
Osteoarthritis treatment
Recipe based on castor oil and gum turpentine. A mixture of two tbsp will help reduce pain syndrome. spoons of castor oil and one tbsp. tablespoons of gum turpentine, which is rubbed with a sore joint in the evening before bedtime. Apply it once every two weeks, because it has a fairly strong effect.
Herbal recipe. To prepare the collection, take in equal proportions nettle and birch leaves, elderberry and calendula flowers, juniper berries, willow and buckthorn bark, horsetail grass. Then 2 tbsp. pour spoons of the mixture with one liter of boiling water, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat under a closed lid for 10 minutes. The collection is allowed to brew for 8-10 hours and filtered. Take half a glass three to four times a day 30 minutes before meals. The duration of the course is three to four months, followed by a monthly break.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is not a defect, and its treatment is possible. But it should be started immediately after the first symptoms appear.
sustavu.ru
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a degenerative disease where the inflammation begins in the cartilage. Over time, it loses its elasticity, becomes thinner. Roughness first appears on the cartilage, then cracks. Further, bone fragments are exposed, rub against each other, since the cartilage disappears altogether. The functions of the joint are impaired, and its deformation begins. All this happens for a long time, gradually, hardly noticeable to humans.
Symptoms can last for several years and get worse. While a person is going to see a doctor, the disease has already developed, he needs treatment for osteoarthritis of the hip joint. Distinguish between unilateral and bilateral osteoarthritis of the hip joint. When both suffer at once, bilateral is diagnosed. This is rare, but ostearthrosis of the hip joint is quite common because the loads are constantly high, therefore deformation occurs.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint is based on premature aging, cartilage degeneration, when the amount of proteglycans in the main part of the cartilage decreases. This is probably why older people are more prone to hip fractures.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the hip joints
There can be many of them, but most often it is the discrepancy between the load and their safety factor. In addition, they affect:
- circulatory disorders, accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products;
- joint overload, overweight;
- hormonal, biochemical changes, injuries, hip fractures;
- infections, inflammations;
- spine diseases: scoliosis, kyphosis; flat feet;
- congenital pathologies, heredity;
- sedentary lifestyle.
Osteoarthritis symptoms
Symptoms of a disease such as deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint depend on the degree of its development. However, the main ones can be distinguished:
- constant pain, disturbing even without exertion;
- stiffness of movements: limping;
- at a later stage, the affected leg becomes slightly shorter than the other;
- muscle atrophy develops.
Often, the first symptoms are ignored by people. In vain, osteoarthritis of the hip joints is better to start treating early. Then there is a better chance of a quick recovery. But they turn to a doctor when the pain is no longer possible to endure, the mobility of the leg is severely limited. Naturally, at this stage, serious treatment is already required.
Degree of osteoarthritis
Usually diagnosed with three degrees of a disease such as osteoarthritis of the hip joints. At grade 1, a person experiences periodic pain only after significant physical exertion. After resting, the pain usually goes away. Other symptoms during the 1st degree of the disease are absent freedom of movement is not limited, the gait remains the same, the muscles are strong. Therefore, the existing symptoms are often ignored, and osteoarthritis of the hip joints gradually develops. Then small bone growths appear, an uneven narrowing of the bone gap, but these changes still do not interfere with a person's life, do not limit mobility.
It is with grade 1 that the disease is most successfully treated.
During the development of grade 2, osteoarthritis of the hip joints manifests itself more seriously. More alarming symptoms appear. The pain becomes more intense, prolonged walking is accompanied by lameness, hip abduction is limited, the muscles that extend the hip lose strength. The head of the femur is deformed, the formation of a cyst is possible, the joint space narrows unevenly. These changes can be viewed on a radiograph.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joints of the 2nd degree, as well as osteoarthritis of the 1st degree, is effectively treated on an outpatient basis, but if a person turns to a doctor in time, he will exactly follow his prescriptions.
At grade 3, osteoarthritis of the hip joints is expressed by constant pain, even during rest - at night. It is impossible for a person to move independently, without the help of a cane. The movements of the joint, hips, buttocks are very limited. The muscles atrophy, the leg becomes shorter, and the gait changes. Bone growths greatly increase, the joint space disappears, the layer of cartilage covering the joint disappears completely, it loses its mobility.
Unlike treatment of 1 and 2 degrees, with 3 degrees of osteoarthritis of the hip joints, it is already necessary to treat only surgically.
But it is still possible to cure the disease, the main thing is to comply with all the conditions of treatment, procedures, and subsequent rehabilitation.
Diagnosis of the disease
When symptoms appear - pain in the hip region, even very short ones, do not postpone a visit to the doctor. To establish an accurate diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hip joints, the doctor will prescribe studies:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- clinical blood test.
The most important thing is to seek help in a timely manner so that osteoarthritis of the hip joints does not develop more than to the 1st degree, then the treatment will be simpler.
Treatment of the disease
If a diagnosis of grade 1 osteoarthritis of the hip joints is made, then the treatment is conservative. Prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondoprotectors, muscle relaxants, etc. They have an analgesic effect, relieve swelling, inflammation, muscle spasm, increase blood circulation, help restore cartilage tissue. Physiotherapy methods give good results:
bolit-sustav.ru
Symptoms and treatment of coxarthrosis of the hip joint 2nd degree
Coxarthrosis, also called osteoarthritis, is one of the most common diseases in modern world... This ailment in the area of the musculoskeletal system can occur both in the elderly and in people under 20 years of age. Osteoarthritis deforms the hip joint, which causes significant problems when moving.
There are two degrees of this disease. And if the first is characterized by the fact that the cause of its occurrence cannot be determined, then coxarthrosis of the second degree develops from diseases such as dislocation of the hip, dysplasia, injuries of the hip joint and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Why might it arise?
There are a lot of reasons why coxarthrosis can develop. One of the most important is sedentary lifestyle... In this case, even after treatment, the disease will return if the lifestyle is not changed. Usually they recommend going in for sports, walking more often, performing a certain set of exercises.
Another reason could be dysplasia of the hip joint and many other hereditary diseases... Also, the development of osteoarthritis can be affected by various injuries, dislocations, bruises. Excessive stress or a sharp change in lifestyle can also lead to deformation of the hip joint.
Coxarthrosis can bother those who have had a hip fracture or have various inflammatory processes in this area. The presence of Perthes disease is another important cause of osteoarthritis.
How to choose orthopedic insoles? Manufacturing to order. Doctors' recommendations: why do knees hurt? How do you find the reason? Read in this article.
Symptoms of the disease
The patient may complain of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the hip, which can radiate to the groin, knee. May be exacerbated by physical activity or during normal life.
- Limp, difficulty bending, and other mobility problems.
- Shortening of the affected limb.
- Weakening and subsequent atrophy of the femoral muscles.
With coxarthrosis, the intensity of pain sensations increases each time. Pain that does not go away even at night can cause sleep disturbances. It is painful sensations that make patients turn to specialists.
Difficulties arise with movement, so patients have to use a cane. This leads to muscle atrophy. And this weakening of the muscles causes mixing of the pelvis, which significantly shortens the injured leg.
How is the disease treated?
You can get rid of this disease with the help of pharmacological drugs. Usually prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs such as ketorol or diclofenac.
They not only reduce the inflammatory and edematous process, but also reduce pain, but in no case should they be used for a long time. The components that make up these drugs reduce the ability of cartilage to regenerate.
So, in order to get rid of this ailment, a number of other remedies should be taken:
- Vasodilator... Such drugs improve blood circulation and this will accelerate the regeneration of cartilage tissue.
- The intensity of pain and muscle tension will help relieve muscle relaxants, the action of which is also to normalize blood flow.
- In order for the cartilaginous tissues to be capable of regeneration, and the degeneration process to stop, it is necessary chondroprotectors... They must be used regularly, and then the regenerative capacity of the cartilage will not be lost even after the drug is stopped.
- Have little effect anti-inflammatory ointments however, they can also have a beneficial effect on the injured limb. Their warming action normalizes blood flow and helps the muscles to relieve spasms. They need to be rubbed in carefully and regularly, since ointments need to overcome a barrier from a sufficiently thick layer of skin to get to the focus of the disease.
Traditional methods
Rich in wellness recipes and ethnoscience... There are three most effective method treatment of osteoarthritis without resorting to medications.
- Coxarthrosis treatment with oils... It is not at all necessary to buy expensive ointments. Oil of eucalyptus, cloves, winter-lovers mixed with aloe juice will help to get rid of coxarthrosis. It is necessary to rub this mixture into the thigh in the morning and in the evening, and to enhance the effect, it is recommended to drink vitamins to strengthen bones and cartilage tissues.
- The most common garlic will help cure coxarthrosis. It is necessary to prepare an infusion of three large lemons, celery root and three heads of garlic. It is better to prepare the infusion in a thermos so that it is infused during the day and remains warm. This broth should be drunk every day in the morning before meals no more than a quarter of a glass.
- So that coxarthrosis does not bother, it is necessary to strengthen the joints. Various chicken broths can help with this, chicken leg broth is especially good in this matter. You can also use an ointment made from pork fat and perestroot.
What to do if joints crunch? Restoring physical activity For what reasons can the shoulder joint hurt? http://jointpain.ru/simptomi/prichini-boley-v-plechevom-sustave Find out the link.
Prevention of coxarthrosis
To figure out what needs to be done to prevent coxarthrosis, you need to remember what are the reasons for its appearance. If it has developed due to a sedentary lifestyle, then the lifestyle should be changed. For example, walking more often, exercising in the gym, doing various exercises at home. Then the blood flow to the hip joints will be normalized and the disease will never return.
Also it is recommended to drink vitamins to strengthen cartilaginous tissues and the musculoskeletal system in general. If pain occurs periodically, then it is necessary to be examined by your doctor at least once a year.
Physiotherapy
How is gymnastics useful for coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree? The fact is that they provide blood flow to the hip joints and prevent muscles from atrophy. Strong muscles are very important in this case, as they prevent the pelvis from moving.
For each patient, his own set of exercises is usually developed, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the development of the disease. However, there are a number of basic movements. All exercises must be performed smoothly, excluding sudden movements, as this can only harm the body.
Also, experts advise swimming in order to prevent this disease. Sea water is very suitable for this, which contains a lot of useful salts and minerals.
Video. Exercises according to the method of Dr. Bubnovsky:
Nutrition rules
For people prone to this disease, there are certain dietary rules. Firstly, meals should be regular, about 5-6 times a day, and portions should be small. The diet should contain proteins that are found in meat, fish and liver. Do not get carried away with boiled eggs, as they contain a large amount of cholesterol. Better to limit their use to 2 per week.
It is necessary to eat legumes and mushrooms so that the body always has a supply of plant proteins. The amount of fat consumed should be strictly limited., but this does not mean that you need to abandon them altogether. Fats help to strengthen the body, and they are best obtained from plant foods and meat.
All health problems can be solved, but you need to take care of it as early as possible. That is why, if there is any tendency to the appearance of coxarthrosis, you must first of all think: why did it appear? And based on this, take appropriate measures.
Video... TV show "Living healthy" with Elena Malysheva on how to overcome coxarthrosis:
jointpain.ru
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint: causes, symptoms. How to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint :: SYL.ru
The sight of an elderly man walking slowly along the street with the help of a cane has become quite familiar to us. But we do not even know what pain and suffering these people are forced to endure. The blame for everything is osteoarthritis of the hip joint - a serious ailment that affects up to 15% of humanity. What is the disease, what are the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment, we will consider in this article.
Osteoarthritis - what is it?
The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body, which accounts for most of the load. It performs the function of connecting the femur to the pelvis. Outwardly, the joint resembles a hinge: a spherical head located in a rounded (acetabular) cavity. Bone mobility is ensured by the cartilaginous surface, which promotes sliding shock absorption and preserves bones from destruction.
With age, the connective tissue loses its ability to retain moisture, becomes thinner and cracks, and the exposed surfaces of the bones begin to rub together. Trying to restore balance, the body increases the production of bone tissue, leading to the formation of growths (osteophytes). They lead to significant deformation of the bones and further impede movement.
When a person develops osteoarthritis of the hip joint, an imbalance arises in the body between the destruction of cartilage and its formation. The basis of the changes is a decrease in the production of proteoglycans (complex protein compounds) by the body, leading to premature aging and degeneration of connective tissue.
People of the older age group are most susceptible to pathology - after forty years. But, since the causes of the disease are many, all age categories suffer from it. Moreover, in women, the disease occurs much more often than in men. This is due to the intense leaching of calcium from the bones, followed by its concentration in the cartilaginous tissue during the postmenopausal period.
The causes of the disease
The disease is often called "coxarthrosis", or "deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint," and is classified as degenerative-dystrophic diseases. Increased stress on the joints is considered a typical cause of the disease. Diseases are most often exposed to people with excess weight, poor posture, as well as after prolonged standing work or prolonged engagement in certain sports (jumping, weightlifting).
Other circumstances contribute to the occurrence of a disease such as osteoarthritis of the hip joint:
- hormonal disruptions;
- genetic predisposition to connective tissue diseases;
- age threshold;
- the presence of certain diseases (psoriasis, arthritis).
How does coxarthrosis manifest?
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint 1 degree. External signs diseases in the initial stage are practically absent. For many years, the disease does not cause much trouble, reminding of itself only with morning and starting stiffness of joints and discomfort.
- ... In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease progresses and brings more and more inconvenience and suffering to the person. Later, during walking or physical activity, the intensity of pain in the upper thigh, radiating to the knee, groin or buttock, becomes more noticeable. After a night's sleep, the negative symptoms disappear.
- Degree 3 osteoarthritis of the hip joint... Gradually progressive disease leads to increased pain and the appearance inflammatory process in the articulation area. Rest no longer brings relief, and cartilage damage is already becoming irreversible. Constant abrasion of the bones makes it difficult or impossible to bend the leg at the hip. To relieve pain, many people try to avoid any physical activity, which negatively affects the muscles. They quickly weaken, and lameness sets in.
What does the disease lead to
Most often, deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint occurs on one joint. Soon, the disease spreads to other parts of the body, which took on the greatest load, in order to alleviate the condition of the diseased joint (knees, feet, spine). Simultaneous involvement of two hip joints does not occur very often.
When the restoration of cartilage tissue becomes impossible, doctors have to resort to at least endoprosthetics. A complex operation helps to avoid disability and can greatly facilitate a person's life.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint significantly increases the risk of serious complications. Many elderly people, mostly of thin physique, are actively developing osteoporosis - the loss of bone strength. Together with coxarthrosis, it can lead to a fracture of the femoral neck. Dangerous injury is difficult to heal and often leads to complete immobility of a person.
Diagnosis of the disease
The first signs of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, manifested in the systematic stiffness of the joints, should immediately alert the person. And if the pain continues to bother for several months, then an urgent visit to a rheumatologist or orthopedist is required. Only a specialist will be able to accurately determine whether a patient has osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
Symptoms need to be described in detail, specifying their frequency and duration. To determine the pain threshold, the doctor performs various manipulations with the hip joint: rotation, flexion and extension of the leg. To assess the external shape of the diseased joint, the doctor may ask the patient to walk or stand on one leg.
To decide how to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint, after an external examination, the doctor prescribes additional studies:
- radiography;
- clinical blood test.
Both hip joints are examined in order to determine the real changes in the joint space, the presence of spines or other pathologies. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can confidently determine the degree of the disease.
Measures to prevent the further development of coxarthrosis
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint is prescribed taking into account the urgent recommendations of the doctor:
- get rid of excess weight;
- balance nutrition;
- intensify physical exercise.
The diet will provide the cartilage tissue with all the necessary elements to maintain it at a quality level. Moreover, proper nutrition will allow you to lose weight. An increase in the consumption of such foods slows down the development of the disease:
syl.ru
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint - treatment, symptoms
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint, otherwise coxarthrosis, is a disease that progresses against the background of tissue changes in the hip joint. Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a degenerative-dystrophic disease, that is, the affected organ becomes incapable of performing its usual functions.
DISEASE PROCESS AND RISK GROUP
In case of illness, the fluid filling the joint changes its properties, gaining excessive density... Thus, the articular cartilage ceases to receive the required amount of lubricating fluid, as a result of which its surface becomes thin due to increased friction. The bone begins to receive a large load, leading to deformation. Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint poses the greatest danger to people:
- in adulthood;
- obese or diabetic;
- have a genetic predisposition or injury;
- athletes receiving a load on the musculoskeletal system.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
The disease affects both sexes, mainly after 40 years. According to statistics, in women, the symptoms of osteoarthritis are more pronounced. The main signs are aching periodic pain.
in the hip region, which are aggravated by physical exertion or in bad weather. A manifestation of coxarthrosis can also be a feeling of rapid fatigue, limping, periodic crunching in the joints, a feeling of heaviness, stiffness, atrophy of the hip muscles.
STAGES OF THE DISEASE
As a rule, deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint is detected in the last stages. , when the pains become more frequent and unbearable. Cartilage under the influence of mechanical stress loses its properties and does not cause pain. Painful sensations arise when non-cartilaginous structures of the joint are included in the process of damage. In the early stages of osteoarthritis, the following symptoms can be traced:
- At osteoarthritis of the hip joint 1 degree pain occurs only in the area of the affected joint, when the patient begins to move after a short-term inactivity, in which the patient does not experience any discomfort. The joint remains mobile, which is typical of any healthy person. X-ray shows only a slight growth of bone tissue, the joint space is practically not narrowed, and there are no changes in the head and neck of the hip bone.
- implies pain radiating to the hip and knee, which bother not only when moving, but in a motionless state. Due to intense exertion, running, long walking, an involuntary limp appears. Changes can be traced on the X-ray - the femur has an uneven contour, the neck thickens, the head is noticeably deformed, and the joint space is narrowed. begins to progress at an increased rate.
- The last 3 stage is characterized by permanent pain, the patient needs support to walk, the pain causes insomnia. The joint gap is even more reduced, the neck of the bone becomes very wide, the head is more deformed.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
The therapeutic complex of measures for coxarthrosis depends on the degree of the disease, on the presence of secondary diseases, and age. However, in general, during treatment, non-hormonal, anti-inflammatory pain relievermeans, means that improve blood circulation in the joints, restore cartilage tissue. To relieve inflammatory processes, it is necessary physiotherapy course(laser therapy, electrophoresis). A course of treatment is used with special equipment for stretching the joint - this helps to relieve the load on the joint.
PHYSICAL EXERCISES
Gymnastics is also necessary for osteoarthritis in the early stages; it is contraindicated to practice through pain. It is better to do classes 2 times a day - in the morning and in the evening. All exercises are performed in a sitting or lying position, since it is in such positions that the load on the affected joints is minimal. Exercise therapy will help keep joints mobile, strengthen muscles and ligaments.
NUTRITION
Due attention should be paid to nutrition with coxarthrosis - correct diet for osteoarthritis of the hip joint warns against obesity, which adds additional stress to the joints. Normal weight prevents the development of the disease - with a weight loss of 5 kg, improvements are observed in 25-40% of patients. The diet implies the exclusion of fatty foods - flour, fatty and sugary foods. It is necessary to replace meat with fish, but if you eat lean meat, eat more cereals and cereals, black bread, vegetables, berries and fruits.
med2health.ru
Osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree of the knee joint Signs, causes, degrees and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee The legs are the part of the musculoskeletal system that is subject to the greatest stress. We travel long distances every day ...
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree treatment Characteristics of osteoarthritis of the knee joint: causes, symptoms, treatment Osteoarthritis (arthrosis) of the knee is a degenerative disease that manifests itself in the defeat of all structures of the joint, leads to ...
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint 1 degree
Osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint 1 degree treatment Degrees, symptoms and treatment of deforming osteoarthritis shoulder joint Osteoarthritis is an ailment that leads to the destruction of joints. Osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint is one of its chronic ...
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint symptoms and treatment Symptoms and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (the second name is deforming arthrosis) is one of the most unpleasant diseases of the joints of the legs. It is a chronic disease ...
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint 1 degree treatment Treatment medications osteoarthritis of the 1st degree of the knee joint Diseases of the organs of the musculoskeletal system today occupy one of the leading places in the general structure of ...
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the 3rd degree treatment Everything you need to know about arthrosis of the knees of the 3rd degree Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (osteoarthritis of the knee / gonoarthrosis) is popularly called salt deposition, which, in fact, is incorrect. Despite the fact that the salt on ...
Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint of the 2nd degree Features of osteoarthritis of the ankle joint Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Often the pathology is accompanied by ...
Bilateral coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree of disability How to get and what gives disability with coxarthrosis of the 2nd degree? Coxarthrosis is the most severe disease of the musculoskeletal system in terms of the course and consequences: it is the deforming coxarthrosis of the pelvis ...
Arthrosis of the ankle joint of the 2nd degree treatment How to cure arthrosis of the ankle joint: advice to the patient Osteoarthritis of the ankle joint is a chronic progressive disease that is not easy to treat. But now there are effective ...
Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint Deforming arthrosis of the hip joint Most diseases of the musculoskeletal system are quite dangerous for humans. Recently, the number of people faced with similar ...
Arthrosis of the ankle joint 1 degree treatment How to cure arthrosis of the ankle joint Ankle joint- one of the most active and loaded joints of the ODS, therefore, problems with it are not uncommon, and at absolutely any age. More often than not ...
Arthrosis of the second degree of the knee joint treatment Have you been informed of arthrosis of the knee joint of the second degree? Our article will calm you down! How can mainstream medicine or folk remedies help? Before finding out, it is worth remembering that arthrosis to ...
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint treatment of the 2nd degree
Deforming arthrosis of the 2nd degree of the knee joint Causes, symptoms, degrees and treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint What is arthrosis of the knee joint? Knee arthrosis is a deformation and destruction of cartilage tissue. Disease...
Nutrition for coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree Symptoms of coxarthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree and its treatment There is practically no cartilage tissue in the diseased joint and the bones are injured Coxarthrosis is a disease that affects the ...
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint is a severe destructive process in which the cartilaginous tissue lining the inner surface of the joint is destroyed. This pathology is the most common among all skeletal lesions. In order for a person not to become disabled, he needs to know how to treat osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
So, osteoarthritis, localized in the hip joint, has a degenerative-dystrophic character. To compensate for damage to the joint, immunity begins to replace the affected areas bone tissue, which grows very strongly. In the joints themselves, serious changes occur that are irreversible. The disease can deform them.
Therapist Elena Vasilievna Malysheva and neurologist Dmitry Nikolaevich Shubin will talk about the disease, how to cope with this condition and at the same time save money:
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women who have already reached the age of 45. This is dictated by hormonal changes in their body, leading to poor absorption of calcium.
The essence of the disease lies in the fact that pathological changes occur in the cartilage tissue, which covers the inner walls of the joints. Due to the deterioration of nutrition, it becomes thin, cracks. Over time, the joint begins to move worse, since the bare surfaces of the bones rub against each other, giving the person unbearable pain. Despite the fact that it will not be possible to completely cure osteoarthritis, proper therapy will slow down its development.
What factors provoke the appearance of pathology?
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint appears due to the effects of such reasons:
- Of advanced age. The processes of natural aging of the body are already involved.
- Prolonged engagement in heavy sports.
- Traumatic injury to the hip joint.
- Excessive body weight.
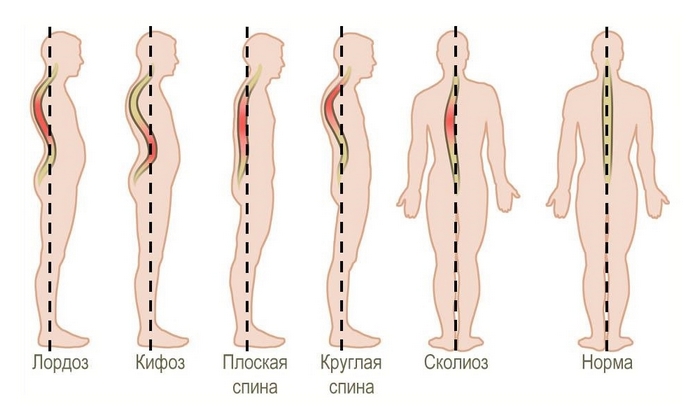
Normal posture and deviations
- Genetic predisposition.
- Hormonal disorders that occur more frequently in women.
- Certain diseases: psoriasis, arthritis.
- Heavy work associated with moving large objects, constant standing on your feet.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
In some cases, osteoarthritis manifests itself in young people who are too active, engage in extreme sports that provoke frequent joint injury. Whatever the cause of the development of the disease, it is necessary to fight it in a timely manner, and by all available methods.
Symptoms and degree of development of the disease
The intensity of the symptoms, as well as the features of their manifestation, depend on the degree of development of osteoarthritis in the patient. Naturally, there are general signs that indicate the presence of a pathological process in the hip joint:
- Severe pain syndrome radiating to the groin area. It occurs not only during movement, but also at rest.
- Severe lameness, as well as a noticeable shortening of the leg on the injured side.
- Weakness of muscles, their atrophy.
- Stiffness of movement.
As for the degrees of development, there are only 3 of them:
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint of the 1st degree is characterized by difficulty in diagnosis, since the disease does not yet have vivid manifestations. It can be confused with other diseases of the supporting apparatus. Due to the fact that the pain is only intermittent and of low intensity, patients are not in a hurry to see a doctor. But the diagnosis can already be made at this stage, since the radiological signs are already visible. The first stage of development is characterized by the following symptoms: a decrease in physical activity, provoking discomfort, pain with increased physical exertion on the hip joint, slight clicks in the hip. At the same time, stiffness of movements is not yet observed.
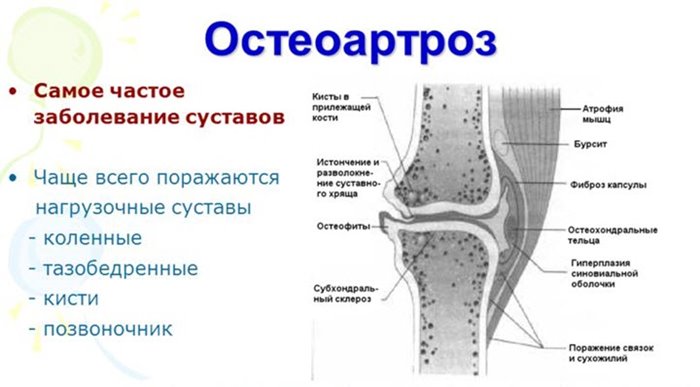
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree. At this stage, patients already more often turn to doctors, since discomfort occurs even at the moment of walking and during examination of the joint. On the X-ray, a 45% narrowing of the joint space is already noticeable. Osteophytes are also found on it. At this stage, the following symptoms can be distinguished: constant pain that radiates to other parts of the body, the patient gets tired quickly, restriction of movement of the joint (stiffness). This stage is also characterized by deformation of the articular surface, discomfort that occurs at the very beginning of limb movement.
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint, grade 3. The X-ray shows the complete disappearance of the joint space. This stage is characterized by the following symptoms: constant pain that does not go away even at rest, a crunch is heard well in the joint, and upon palpation, the patient feels very strong and acute pain. Deformation of the hip joint is visible to the naked eye. It is very difficult for the patient to move. He uses a cane to walk. In most cases, mobility disappears altogether.
The left or right joint is usually affected. In addition, polyosteoarthritis is often diagnosed - a lesion of both joints. Treatment of this deforming disease should be started as soon as the first signs appear. Naturally, it is imperative to determine the reasons for its development.
Features of the diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Not every patient applies for medical help as soon as you feel the first discomfort. This seriously complicates further treatment and disrupts the person's quality of life. Therefore, you need to go to the doctor as soon as you felt stiffness in movements. To determine an accurate diagnosis, specialists perform a comprehensive examination of the patient. It includes:
- Physiological tests to determine the level of pain threshold.
Hip ultrasound procedure
- General and biochemical blood test.
- X-ray of the hip joint.
The diagnosis of DOA is made only after examining the right and left joints simultaneously.
Deforming osteoarthritis (DOA): features of the disease
To combat osteoarthritis of the hip joint, it is not necessary to go to a hospital. Pathology treatment is aimed at:
- Reducing the intensity of pain.
- Reducing the inflammatory process in the affected hip joint.
Traumatologist-orthopedist Anton Pavlovich Khapilin tells more about the causes and description of the disease:
- Improving joint mobility.
- Stimulation of metabolic processes and blood circulation in tissues.
Treatment of polyosteoarthritis involves not only the use medications, but also the use of physiotherapeutic procedures, therapeutic exercises, as well as visits to sanatoriums and resorts of a narrow focus. In the last stages of the development of DOA, the patient may be recommended to have surgery to replace the affected joint.
What is deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint?
Any degenerative disease of the supporting apparatus can deform it. DOA is a slowly progressive and periodically recurrent pathology that leads to persistent impairment of the functionality of the joint. Deforming osteoarthritis is one of the first places among other skeletal lesions in terms of prevalence. It is not possible to completely cure it.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint provokes excessive stress, injury to the joint, as well as inflammatory and infectious processes in the body.
There are 2 types of pathology:
- Arising against the background of excessive load and affecting the joint not affected by other diseases.
- Developing as a result of damage to the joint by other pathological processes.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint
Pharmacy medicines, massage, home remedies, physiotherapy, physiotherapy complexes are used to treat the disease and improve the patient's quality of life. Proper nutrition is also very important.
Features of the use of drug therapy
So, initially, treatment involves the elimination of unpleasant symptoms. The patient is prescribed the following medications:
- NSAIDs: Ibuprofen, Naproxen. These funds effectively relieve pain and reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process. With polyosteoarthritis, such drugs are prescribed only by a doctor. He also determines the duration of their use. These drugs can cause side effects.
- Corticosteroid injections: Kenalog, Dexazon. The injection is made directly into the affected left or right joint. You can use this method of blocking pain syndrome only a few times a year, but it works instantly.
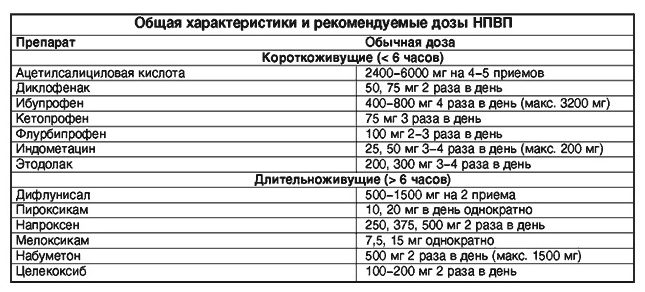
- : "Artra", "Don" and others. Unlike previous remedies, they do not easily eliminate symptoms, but they are also able to treat pathology. But they will be effective only in the first stages of the development of polyarthrosis, when there is still cartilaginous tissue in the joint. A drug that combines chondroitin and glucosamine is quite high quality. Treatment of osteoarthritis deformans with chondroprotectors lasts at least 3 months.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents: "Lyoton", "Kurantil". The presented drugs improve blood microcirculation in the affected joint, which increases the effectiveness of the treatment of deforming osteoarthritis.
- Local ointments and lotions with Dimexidum.
During therapy, the affected joint should not experience increased stress.
Other treatments
In addition to pills, the patient is also prescribed physiotherapy procedures. They help restore joint mobility and functionality. Electrophoresis with Dimexide is very useful. Good feedback also has laser treatment. It is also recommended for the patient to visit the pool for recovery.
For the correct treatment of the disease, it is important to follow the correct diet and a specific diet. It is advisable to exclude fatty, meat and sweet foods from the diet. The diet involves the use a large number vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products. Garlic and onions should be included in the diet. The diet usually lacks potatoes, tomatoes, egg yolk.
Doctor-rheumatologist Maria Eduardovna Tsanyan on the treatment of the disease:
It helps to restore the affected joint physiotherapy... The set of exercises is selected by the doctor. Physiotherapy exercises strengthens muscles and prevents them from atrophy. The following exercises are considered useful for polyarthrosis: circular movements of the legs, flexion and extension of the limbs, imitation or real cycling. If exercise therapy exercises are not effective, then the patient may be assigned to traction of the joint.
Features of surgery
If the injections and pills do not help, and the disease itself is in an already advanced form, the patient is prescribed surgery... Since the disease can severely deform the joint, the patient may need to completely replace it. But this operation is considered to be very difficult.
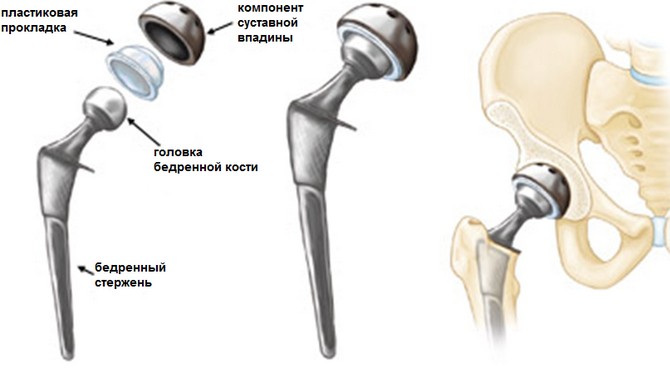
Hip arthroplasty
A complication of the intervention can be a hip fracture, after which recovery is difficult and takes a very long time. In this case, the cartilage tissue almost completely loses its properties.
Alternative treatment of osteoarthritis deformans
Injections and pills are just a part complex therapy... Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip joint is additionally performed with the help of folk remedies. Naturally, they must be agreed with the attending physician. These homemade recipes will be helpful:
- A mixture of honey, mustard and vegetable oil. All ingredients are taken in a tablespoon. They need to be put in an enamel container and brought to a boil, then cooled and filtered. This homemade compound is used as a compress that lasts for 2 hours on the affected joint.
- To reduce pain syndrome will allow a kind folk ointment based on castor oil (2 tablespoons) and turpentine from resin (1 large spoon). After preparing the medicine, it is used to rub the sore spot before bedtime. It is necessary to treat polyarthrosis in this way for 1-2 weeks.

Gum is a resinous substance released from the trunks of coniferous trees when cut
However, only homemade ointments will be ineffective. The disease must be fought in a complex manner.
How to prevent pathology?
It is almost impossible to completely cure osteoarthritis that has already appeared. Therefore, you need to try, in general, to prevent its appearance. Preventive measures are as follows:
- You should not be in a sitting position for a long time. Even if the position provides for sedentary work, a person needs to periodically perform a complex of simple gymnastics, warm up.
- Swimming is considered useful for the prevention of deforming osteoarthritis.
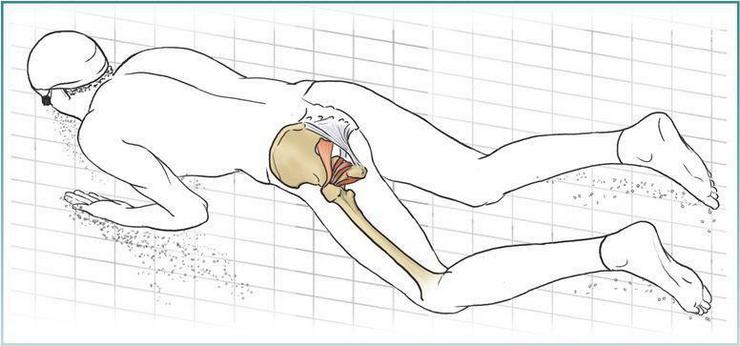
Benefits of swimming for joints
- Physiotherapy is used not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of disease. The exercise therapy complex is selected by a doctor.
- It is important to follow the principles of rational and proper nutrition.
In the presence of osteoarthritis of the hip joint, all available methods are used for treatment. Exercise therapy in combination with drug therapy, physiotherapy can restore the functionality of the joint and improve the patient's quality of life.
