A sedentary lifestyle, typical for office workers and those who like to relax in front of the TV or behind the monitor screen, often becomes the cause of the occurrence. The first signs of this disease can appear as early as 25 years and, if left untreated, complications can lead to serious consequences.
In the article we will consider what osteochondrosis is. cervical spine, the main causes of this disease, its symptoms and stages, methods of treatment, as well as answer other questions that arise in patients with osteochondrosis.
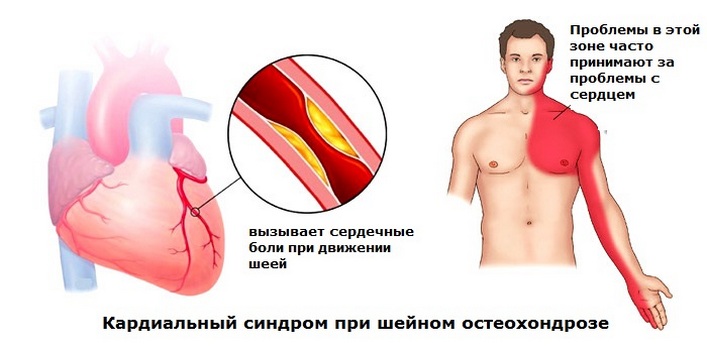
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine (Osteohondroz) - these are degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the intervertebral discs, as a result of which the discs themselves, vertebrae and joints of the cervical spine are damaged, there is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs. The disease progresses if left untreated and can lead to headaches , circulatory disorders and even hernia ... As well as, the disease occurs due to a violation of mineral metabolism, as a result of which the bones and joints become weaker.
Osteochondrosis can cause instability of the cervical spine (symptoms and treatment are similar to chondrosis , but have a number of features), which is often accompanied by displacement of the vertebrae. In turn, this accelerates the development of osteochondrosis, destroying the vertebral section.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The main reasons that can cause osteochondrosis:
- improper nutrition and;
- posture disorders;
- sedentary lifestyle: sedentary work (drivers, office workers), lack of physical activity, etc.;
- suffered injuries in the neck, spinal injuries;
- too much physical activity, unusual for the body;
- nervous tension, frequent stress;
- hereditary predisposition to the development of the disease;
- abnormal development of the cervical spine.
Most of the above causes stress on the cervical vertebrae, resulting in muscle spasm ... Because of this, the blood circulation process is disrupted, the efficiency of metabolic processes decreases, which causes degenerative changes. The structure of the intervertebral discs changes, they become thinner and deformed, protruding beyond the spine.
Often the cause of osteochondrosis is progressive discosis that has spread to adjacent vertebrae or bone. It occurs most often during prolonged physical exertion in the lumbar and cervical regions, almost never touching the chest.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
While developing, osteochondrosis goes through several stages, characterized by certain signs and symptoms. We will consider these stages below.
Osteochondrosis of the 1st degree of the cervical spine (preclinical stage)
Usually, at the initial stage of the development of the disease, only slight smoothness is observed. lordosis of the neck , patients experience pain, aggravated by turning and tilting the head, feel tension and rapid fatigability of the muscles in the back, lumbar region. At this stage, osteochondrosis can be cured without medication, it is enough to change the diet, exercise and other activities.
Degree osteochondrosis
In the second stage, instability is observed between the vertebrae, the patient begins to worry about more intense pain, periodically radiating to the arms or shoulders, also intensifies pain when turning and tilting the head. This occurs as a result of nerve entrapment, as the height of the intervertebral discs decreases. Patients begin to notice rapid fatigue, absent-mindedness, decreased performance and headaches.
Osteochondrosis grade 3
At this stage, the pain begins to intensify, it constantly arises not only in the neck, but also in the shoulders, gives it to the hands. The arm muscles become weaker and numbness is observed as they begin to form. In this case, the diagnosis reveals low mobility of the cervical spine. Patients are also worried about weakness.
Osteochondrosis grade 4
At the final stage, the intervertebral discs are destroyed, which are replaced by connective tissue. The pathological process affects several segments of the ridge at once, which may be at different stages of destruction. Patients have a lack of coordination, dizziness and pain increase, tinnitus and other disorders appear.
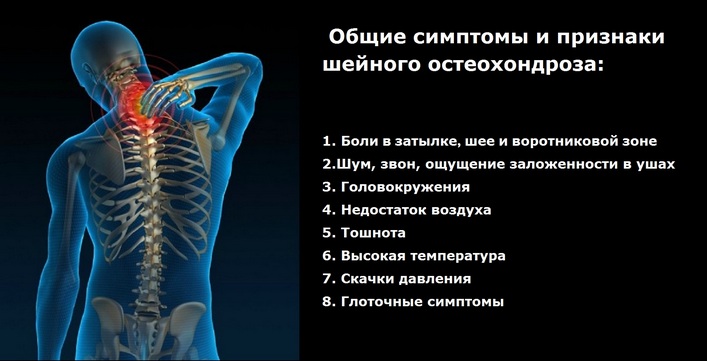
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Even the initial stage of the disease can be identified by the following signs:

- pain in the neck, back of the head, shoulders or arms;
- weakness in the arms;
- crunching and pain with head movements;
- general weakness, fatigue, impaired coordination, dizziness;
- decreased visual acuity and hearing, numbness of the tongue.
One of the most common symptoms is with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. At the same time, the symptoms of dizziness can be accompanied by noise and ringing in the ears (hearing acuity is reduced), sensations, as well as nausea and vomit ... Treatment of vertigo with cervical osteochondrosis does not require any special methods and drugs and occurs in parallel with general therapy. At the same time, it is the doctor who determines how to treat these symptoms - one should not try to get rid of dizziness using folk methods.
Another unpleasant consequence is frequent, especially in women. Migraines can occur several times a day, causing unpleasant and painful sensations.
Signs of cervical spine disease manifest themselves somewhat differently than osteochondrosis in other parts of the spine due to the fact that the vertebrae in the neck area are close to each other, the height of the intervertebral discs is small, which leads to complications even with minor degenerative changes.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis arising in the brain
With the development of osteochondrosis, the flow of blood to the brain stem through the arteries, which are compressed by the protruding edges of the vertebrae, decreases. As a result, there is a violation of the blood circulation in the brain. Patients have neurotic disorders: irritability , anxiety , frequent mood swings, touchiness, reduced ability to concentrate. In some cases, outbursts of anger, fear, melancholy may occur.
Vascular spasms can lead to fainting, headache, is observed noise in ears , the appearance of dots before the eyes. Another consequence of osteochondrosis may be damage to the vestibular apparatus. In this case, the following exacerbation symptoms appear: dizziness , feeling unsteady , nausea , in some cases - vomit .
Symptoms of cervical chondrosis in women
In general, the signs of osteochondrosis are the same for men and women. However, women between the ages of 45 and 65 often experience discomfort, pain, and numbness, accompanied by tingling, in the arms during sleep. Such attacks can be repeated several times at night.
Diagnostics of the chondrosis of the cervical spine
To diagnose a disease in medicine, the following methods are used:
- X-ray... This method is ineffective, especially in the last stages of the development of osteochondrosis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)... A method that allows you to see bone structures, herniated intervertebral discs, their size and direction of development.
- CT scan... Less effective solution than MRI, as the presence and size of hernias is difficult to determine.
- Ultrasonic duplex scanning... This method is used in cases where a disturbance in blood flow is suspected in the arteries. With the help of a scan, you can determine the speed of blood flow and whether there are obstacles to it.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
For the treatment of a disease such as osteochondrosis, they are used different methods: medications, physiotherapy, massage of the cervical-collar zone for blood supply to the brain and physiotherapy, further observance proper nutrition... It is the combination of all methods how to treat cervical chondrosis, will allow you to achieve real results in the fight against the disease.
Despite the fact that women are more prone to headaches and numbness of the extremities with this disease, the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in women is no different from its treatment in men: the same drugs and exercises are prescribed.
First aid for severe pain
Distractions are often used, such as , which does not heal, but only warms up the inflamed area and distracts from pain. In case of edema in the area of inflammation, the patient can drink an infusion of herbs or a diuretic for 3-4 days. Is it possible to cure osteochondrosis with such methods? These measures are only temporary; to treat the causes, you need to see a doctor.
It should be noted which doctor treats osteochondrosis. If you suspect that the causes of pain in the cervical spine are the occurrence of osteochondrosis, you should contact neuropathologist ... It is this specialist who deals with diseases of this kind. In some medical institutions there are narrowly focused specialists dealing specifically with diseases of the spine. If your clinic has vertebrologist Milgamma and other medicines.
Taking pills for osteochondrosis, it should be remembered that a significant effect of drug treatment with pills will be only if you combine it with other methods, including exercise. It should also be noted that the attending physician must prescribe how to treat the disease based on its stage and other signs.
Many doctors consider the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with injections to be effective, since this allows faster action on the endings of the nerves and causes a minimum of side reactions. Wherein vitamins best taken in pill form as there is no difference to digestion, but injections can be painful.
Injections used for treatment:
- intramuscular injections cause a general strengthening and anti-inflammatory effect ( Baralgin , Analgin , Mydocalm , Ibuprofen , Ketorolac , Ambene );
- blockades are injected directly into the affected area, which leads to a quick effect.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Therapeutic gymnastics brings the maximum effect and is the safest during the recovery period. When performing exercise therapy exercises, the patient should not experience pain or discomfort.

Exercises for the cervical spine are aimed at strengthening the muscles of the neck, which will not only overcome the disease, but also serve as prevention for its occurrence.
| Exercise number 1 | From a prone position on a living, hands rested on the floor, slowly raise your head, torso, while your back must remain straight. In this position, linger for 1-2 minutes, then slowly lower yourself to the floor to the starting position. Repeat the exercise 2-3 times. |
| Exercise number 2 | Lying on your stomach, arms extended along the body, turn your head first to the left, while trying to touch the floor with your ear, then repeat, turning your head to the right. Do at least 6 repetitions on each side. |
| Exercise number 3 | Sitting on the floor, bend down as you inhale, while you need to touch your chin to your chest, then as you exhale, lean back and throw your head back. Repeat the exercise 10 to 15 times. |
| Exercise number 4 | The palms are attached to the forehead, while it is necessary to press with the palms on the forehead, and resist with the forehead, pressing on the palms for 30 seconds. Then perform the exercise, pressing with clasped hands on the back of the head. Repeat 2 or 3 times. |
| Exercise number 5 | Slow rotation of the head in different directions. Performed 10 times on each side. When doing this exercise, it is important that dizziness does not appear, otherwise it is necessary to stop the exercise. |

For clarity and more accurate performance, we present a video of exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at home
Home treatment methods are only an addition to the complex prescribed by the doctor, and they will not help completely get rid of the disease. Before treating osteochondrosis at home, be sure to consult a doctor so that he can diagnose and prescribe the necessary medications. It is the doctor who must determine how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at home
For home treatment are used: recipes traditional medicine(designed to relieve pain and muscle tension, improve blood circulation), physiotherapy exercises, as well as mandatory massage of the neck and collar zone at home.
Folk recipes for relieving pain in the neck area:
- Place a sheet of horseradish with the inside of your neck, secure with a bandage or any breathable cloth. Before use, it must be scalded with boiling water and cooled to room temperature. It is advisable to perform at bedtime and leave the bandage on overnight.
- Chop the potatoes finely and mix in equal proportions with honey. The mixture will be similar in consistency to an ointment. Use as a compress at least once a week.
- Well relieve the pain of warming up. For this purpose, you can use mustard plasters, a bag of heated sand, pepper plasters or alcohol.
It is not uncommon for patients to start looking for ways to treat or relieve pain in various forums and similar sources. It should be noted that not a single forum and its visitors will be able to correctly diagnose the stage of the disease and the methods of its treatment. The question of whether osteochondrosis is treated in your case and how it should be done should be decided by a qualified doctor on the basis of diagnosis.
Therapeutic massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Massage is necessary to strengthen muscle tone and relieve pain. Depending on the stage at which the osteochondrosis is, the massage technique is selected. Nevertheless, when doing neck massage, specialists use all the techniques of classical massage: trituration , stroking , kneading etc. In cases where the patient has pain on only one side, the massage begins in the healthy part of the neck, gradually moving to that part of the collar zone where painful sensations arise.
Massage can be performed at home, but very carefully so as not to aggravate and harm the patient. The patient should take a prone position, put the forehead on the hands and stretch the chin towards the chest. In this case, the muscles of the neck should be completely relaxed.
| Stroking | It is necessary to start the massage with these movements: stroking the collar zone in the direction from the lymph to the supraclavicular and axillary nodes. Then flat and comb-like strokes are applied. |
| Push-ups | To perform push-ups, the masseur places a hand across the neck (index and thumbs while they should be together) and moves down the spine. Also, push-ups can be performed with the edge of the palm up to the shoulder joints. |
| Trituration | Rubbing is done to warm up the muscles, relax them, and improve blood flow to the area. Massage should begin from the base of the skull, performing circular and rectilinear movements with your fingers. You can also perform sawing movements with palms parallel to the ribs. |
| Kneading | Kneading should be performed on the neck in a circular motion. |
| Vibration | The massage ends with strokes and vibration, which is performed with the help of shaking and beating. |
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra
To prevent the onset and development of the disease, doctors recommend adhering to simple rules:
- go in for sports (especially effective swimming );
- include in the diet foods containing a large number of magnesium and calcium (fish and other seafood, beans, peas, nuts, seeds, dairy products and cheeses, spinach, etc., do not use hot peppers, salted, grapes, sugar, flour products, smoked products);
- during sedentary work, do a warm-up several times during the day;
- choose a comfortable pillow and mattress.
The article examined the causes, symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, ranging from medical intervention to home receptions. It is possible to cure this disease, including without surgery, but all methods should be used for this: taking medications, doing exercises and doing massage.
Osteochondrosis today is rightfully considered a "disease of the century", because most often it affects people whose work does not require increased physical activity.
In most cases, changes in cartilage and bone tissue observed in people of working age - up to 40 years.
The disease can affect different parts of the spine, and the second most common is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Osteochondrosis is a dystrophic disorder of the articular cartilage and adjacent bone tissue.
Previously, the term was applied to a large group of osteoarticular diseases, but now it is used only for degenerative diseases of the spine.
Compared to other parts of the spine, the cervical region is the most mobile and has many nerve and vascular formations. The structure of the vertebrae is small in size, as well as in the fact that they are surrounded by a rather weak muscle corset.
This anatomical structure predisposes to the development of osteochondrosis, the severity of clinical manifestations of which depends on the nature of changes in the intervertebral discs and the degree of their destruction.
The reasons for the development of the disease
The main and most common cause of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a sedentary lifestyle.
Due to a lack of physical activity with a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle:
- metabolic processes are disrupted;
- the level of salts in the bloodstream and lymphatic fluid increases;
- in the cervical spine, in the kidneys and liver of the spine, salts are deposited.
Damage to the cervical vertebrae is mainly caused by a lack of nutrients in the intervertebral discs. Therefore, the main reasons for the occurrence of cervical osteochondrosis also include improper and unbalanced nutrition.
Risk factors
There are many risk factors for cervical osteochondrosis.

The most common factors are:
- heredity;
- age-related changes;
- injuries of the cervical spine;
- hypothermia;
- hormonal disorders that lead to metabolic disorders;
- some autoimmune diseases that damage cartilage tissue (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism).
Why is it dangerous?
Not only the spinal cord and nerve roots pass through the cervical spine, but also the vertebral artery, which is responsible for supplying blood to the back of the brain, medulla oblongata and cerebellum.
Therefore, with cervical osteochondrosis, this artery is squeezed, and as a result, cerebral circulation is impaired.
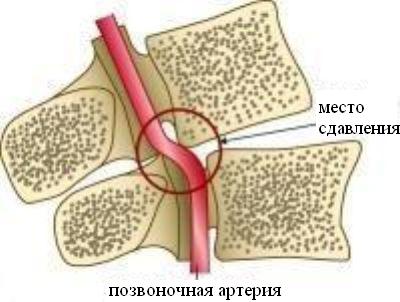
Figure: Vertebral artery syndrome
In especially advanced cases, compression of the artery and adjacent blood vessels and nerve plexuses can lead to such consequences as:
- lack of coordination;
- loss of hearing and vision;
- stroke.
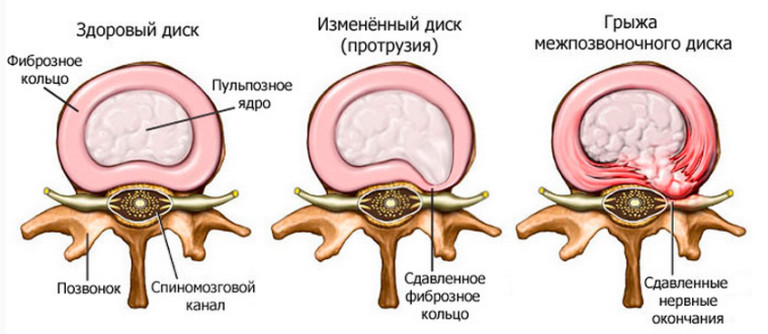
If the disease is not cured at the initial stage, this can lead to complications such as protrusion of the intervertebral disc or herniated disc.
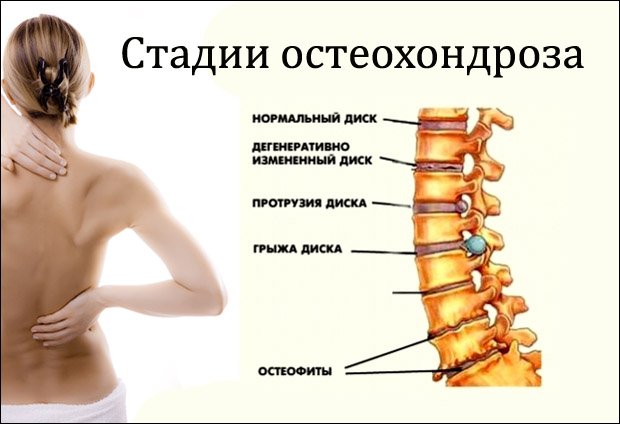
The degree of development of the disease
Cervical osteochondrosis, like osteochondrosis of other parts of the spine, develops in stages. There are 3 stages of the development of the disease.
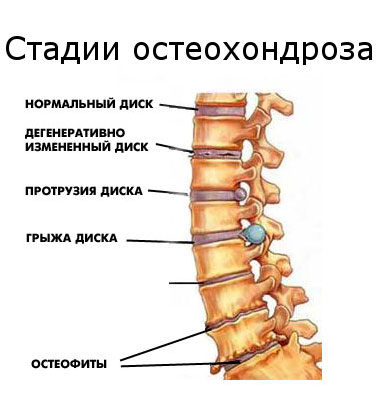
Fig .: stages of osteochondrosis
1st degree
It is characterized by the onset of destruction of the intervertebral discs.
Cracks form in the annulus fibrosus, the strength and elasticity of the disc is disturbed, its height decreases, due to which the nerve roots are compressed.
A characteristic aching pain appears. Sometimes at stage 1 (preclinical) such pain may be absent, and osteochondrosis occurs with moderate discomfort in the neck.
2nd degree
If osteochondrosis of the 1st degree was not treated or the treatment was not effective, then a chronic condition arises, which is the 2nd degree of osteochondrosis.
The pain becomes constant, the destruction and compaction of the intervertebral disc continues and leads to minor dislocations of the cervical vertebrae.
With cervical osteochondrosis at this stage, falling head syndrome may develop. This syndrome is characterized by severe pain, and the person has to keep the head in a fixed position to reduce the pain.
Grade 3
Cervical osteochondrosis of grade 3 is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- headaches;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- cervical "lumbago";
- violation of the sensitivity of the upper limbs.

The annulus fibrosus is almost destroyed, which leads to complications of osteochondrosis - protrusion of the intervertebral disc or intervertebral hernia.
At stage 3 of osteochondrosis, the intensity of pain may decrease, since the affected cartilaginous tissue in the intervertebral disc simply does not exist anymore, which means that there is no source of pain, but the pinching of the nerve roots remains, so the pain does not completely go away.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
There are many signs of this disease. And they depend on which vertebrae are damaged by this disease.
Typical syndromes in cervical osteochondrosis are:
- radicular syndrome;
- cervical migraine syndrome;
- hypertensive syndrome.
All these syndromes are accompanied, first of all, by different types of pain.
If we consider the syndrome of the vertebral artery, then the headache is manifested here already at an early stage of the development of the disease.
In this case, attacks of pain may be accompanied by:
- dizziness;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- visual symptoms (the appearance of fog before the eyes, decreased visual acuity, etc.). fainting (with sudden head movements).

In hypertensive syndrome, increased intracranial pressure is determined.
The headache is more of a bursting character, may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. With an exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, an increase in temperature and an increase in ESR may be observed.
When the spinal roots are compressed ("radicular syndrome"), the following neurological symptoms may appear:
- severe pain in the neck (cervicalgia);
- neck pain that spreads to the forearm and humerus (cervicobrachialgia);
- pain in the arm;
- a crunching or cracking sensation in the neck when turning the head;
- pain "radiating" to the ear, which occurs after a long stay in an uncomfortable position or sudden movement;
- pain or feeling of a lump in the throat, breathing problems;
- numbness of hands and tongue;
- a feeling of swelling of the tongue;
- severe weakness;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- noise in ears;
- general deterioration in well-being.
In the syndrome of "cervical migraine", irritation of the sympathetic nodes is observed, which leads to a violation of the reactivity of the vessels of the brain and impaired blood circulation.
As a result, hypertension may develop, often accompanied by:
- congestion in the ears;
- tachycardia;
- noise in the head;
- ringing in the ears.
When the arteries that supply the spinal cord are compressed, a spinal stroke can occur.
Violation of blood circulation in the brain with osteochondrosis can lead to:
- oxygen deficiency of brain cells;
- mental disorders (depression, panic attacks);
- the appearance of signs of epilepsy, such as short-term loss of consciousness and tension of the whole body - they are often confused with signs of epilepsy.
A very common symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is changes and disturbances in the rhythm of the heart, for example, extrasystole or arrhythmia.
Such signs are very common among drivers and office workers.
Due to a sedentary lifestyle, changes occur in the intervertebral discs of the cervical and thoracic spine, which lead to disturbances in the work of the heart.
In most cases, until osteochondrosis is cured, it is virtually impossible to get rid of heart rhythm disturbances.
Swelling under the eyes can also indicate osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Most often they depend on the position of the head during a night's sleep, disappear during the day and are combined with headaches, dizziness, heaviness in the head, etc.
Vegetovascular dystonia is another common disease that occurs with this disease.
It is a consequence of pinching of the vascular arteries that run along the sides of the spinal column.
Diagnostic methods
The preliminary diagnosis is established by a neurologist during the initial examination of the patient. More recently, the doctor had to make a diagnosis by conducting only an external examination of the patient and sending him to an x-ray.
But, unfortunately, it is impossible to see the full picture of the development of the disease on an X-ray.

Currently, such examinations as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are available, with the help of which it is possible to fully assess at what stage of development the disease is.
After the diagnosis is made, the patient is referred to a doctor who specializes in this area.
Which doctor is treating?
The treatment is carried out by a specialist of a narrow focus - a vertebrologist or a vertebroneurologist.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The basis for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is the severity of the main clinical symptoms.
In the cervical spine, symptoms are mainly associated with squeezing of blood vessels and nerve endings, therefore, during treatment, edema is first of all relieved and blood circulation restored.
There are many treatment methods used in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
The most effective treatment is complex, which is a combination of several conservative methods treatment.
Complex treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can include the following traditional and non-traditional methods: drug treatment, massage, acupressure, manual therapy, physiotherapy, acupuncture, homeopathy, folk remedies, etc.
The main stages of treatment for osteochondrosis are the same for all localizations of this disease:
- First you need to relieve pain.
- Then the swelling will be removed.
- At this stage, it is necessary to normalize blood circulation.
- Strengthening the muscle corset.
- Improving nutrition and tissue regeneration.
Only a team of good specialists can choose the most suitable therapy, which includes a neurologist, physiotherapist, massage therapist, surgeon, and vertebral neurologist.
Like any disease, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be treated at the earliest stage of its onset. If you do not start the process, then at this stage you can achieve a complete cure of osteochondrosis.
Unfortunately, stages 2 and 3 of cervical osteochondrosis are accompanied by complete or partial destruction of the intervertebral discs, therefore, these stages are characterized by a very long recovery process.
First aid
How to relieve pain during exacerbation?
At severe pain you need to take a pain reliever from your home first-aid kit: it can be analgesics - diclofenac, nise, etc. You can also stick a pepper plaster for pain.
If swelling occurs, diuretics can be taken. Rubbing the neck with pain-relieving ointments may help.
Also, for pain, you can use which:
- relieves pain in the spine;
- reduces muscle spasm;
- stimulates the work of internal organs;
- normalizes blood circulation.
Physiotherapy exercises during exacerbations are contraindicated, as well as warming up, since these effects can cause serious complications.
After the removal of acute pain, it is necessary to urgently consult your doctor for advice.
Medication treatment
Treatment with medicines most often begins with injections (with an exacerbation), then they switch to tablets and suppositories in combination with the local application of ointments and gels.
Anesthesia during drug treatment is performed using steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, diclac gel, etc.).

Photo: diclak gel for the treatment of osteochondrosis
Be sure to prescribe funds that restore cerebral circulation.
With pathological muscle tension, muscle relaxants, such as Mydocalm, can be prescribed. For more effective treatment vitamins in a therapeutic dose and microelements are taken.

Massage and self-massage
This method works well with physical therapy and physiotherapy. You can take a massage course either in any medical institution or by contacting private practices.
Massage is necessary for cervical osteochondrosis to strengthen the muscles and to relieve tension in the neck.
The task of the masseur is to remove harmful products metabolism, as well as relieve spasm from the pathology zone.
The main techniques used by specialists in neck massage are:
- stroking;
- squeezing;
- trituration;
- vibration;
- kneading.
The self-massage technique can be performed using the following techniques:
- stroking (movements should be soft, without much effort, forming folds)
- kneading (deep impact on the muscles, by grabbing into a fold, pressing and pushing up);
- vibration (vibrational impact by beating, shaking, patting).
Self-massage should always be finished with stroking. During vibration, you can use a massager.
Video: self-massage of the neck
Acupressure
 Acupressure massage relieves headache well with exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, helps with pressure surges, normalizing it.
Acupressure massage relieves headache well with exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, helps with pressure surges, normalizing it.
Scheme of acupressure:
- Impact on the feng fu point, which is located under the occipital protuberance, for 1 minute.
- Impact on the feng chi point, located two fingers wide from the mastoid processes of the skull.
- Impact for 1-1.5 minutes on the ya-men point (located at a distance of three fingers from the feng fu point).
- Sedation for 1-1.5 minutes on the da-chzhui point (7th cervical vertebra).
After the acupressure, you need to lie down for a few minutes, as you may experience slight dizziness.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy helps to cope with both acute and chronic pain, it also increases the range of motion and improves posture well.
The main methods of manual therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- Relaxing and segmental massage. It is used to warm up muscles and relieve tension.
- Mobilization. Actions aimed at restoring the functions of the joints. by stretching method.
- Manipulation. A sharp push directed at the pathological areas of the patient. The procedure is accompanied by a characteristic crunch (return of the joint to its normal position).
A specialist practicing manual therapy should be fluent in these techniques. Otherwise, any mistake can lead to injury.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture promotes the release of cortisol into the bloodstream. This hormone has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.

Acupuncture is performed by affecting points near the inner edge of the scapula. The needles are inserted to a depth of 1 to 2 cm and left to act for 10 to 30 minutes.
Video: about the benefits of acupuncture
Homeopathy
Medical treatment carries with it many adverse side effects, so homeopathy can be a worthy substitute for treatment without undesirable consequences.
With this ailment, the following homeopathic medicines are most often used:
- Rus in 6, 12 and 30 dilutions, as well as in the form of ointment and oil;
- Staphysagria in 3 and 3 dilutions.

For cervical osteochondrosis with severe hypertension (expressed by pain in the back of the head), strontium carbonate or Stontian Carbonic is used.
Assign in 3, 6, 12 and 30 dilutions.
With a combination of cervical osteochondrosis with varicose veins, Esculus is prescribed in 3, 3 and 6 dilutions.
Power features
Food should be rich in calcium and magnesium.
These micronutrients are found in fish and seafood, nuts, legumes, and dairy products. 
Often, osteochondrosis of the neck can be accompanied by atherosclerosis. In this case, a strict diet is recommended.
The diet is prescribed for 3-4 months. It is necessary to limit the consumption of all foods containing cholesterol. These include animal fats, fatty meats, fatty dairy products, etc. You should also limit or exclude the consumption of salt, sugar, flour products.

Cervical osteochondrosis and alcohol are interconnected. The fact is that getting into the blood, alcohol destroys cells, thereby aggravating the already impaired blood circulation in osteochondrosis.
Therefore, it should be limited to a minimum, and in the period of exacerbation, completely stop drinking alcohol.
Disease prevention
To prevent cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended to observe the following rules:
- sleep should be on a firm mattress and on a low pillow: the neck flexion angle should not be more than 15 degrees;
- take a hot shower every day for at least 10 minutes;
- visit the sauna and bathhouse as often as possible: heat helps relieve neck spasms;
- give yourself aerobic activity and regular walks at a low pace;
- go swimming;
- after 25 years, avoid shock load on the spine (jumping, running);
- when sedentary, be sure to take five-minute breaks every hour;
- regular yoga classes can prevent any manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis;
- refuse to visit the gym, as bodybuilding classes can provoke the occurrence of cervical disc protrusion;
- exercise as a prophylaxis for osteochondrosis of the neck helps to strengthen cervical muscles, relieve tension.
Frequently asked Questions
What to do during pregnancy and how to treat it?
Often, it is during pregnancy that the first symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis occur.
This is due to a change in hormonal levels and softening of the vertebrae, as well as due to a shift in the center of gravity and excessive stress on the spine.
Treatment of osteochondrosis in pregnant women is quite difficult, since it is limited mainly by the drug method aimed at relieving pain.
You can use natural ointments or resort to traditional medicine.
Any impact on the neck area (warming up, exercising, etc.) during pregnancy is strictly prohibited.
Does it happen in children and adolescents?
In children and adolescents, cervical osteochondrosis develops as a result of congenital or acquired functional insufficiency of cartilage tissue.
It is expressed by complaints of headache, fatigue, dizziness and fainting.
Can the neck area be warmed up?
Warming up the neck with cervical osteochondrosis is strictly prohibited, especially in the stage of exacerbation of the disease, since warming up can lead to an increase in edema and vasodilation of the brain.
How to sleep properly?
You need to sleep on a flat, hard bed with an orthopedic mattress.

The use of an orthopedic pillow helps to relax the muscles in the cervical spine, reduces irritation of the nerve endings, which prevents headaches and insomnia.
Are physical activities and sauna allowed?
In preventive measures and at stage 1 of cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended to engage in physiotherapy exercises, swimming.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at home carried out under the supervision of a doctor. The main danger of the disease is that it does not appear immediately. The development of cervical osteochondrosis can be asymptomatic for quite a long time. At an early stage, deliver correct diagnosis rather difficult as clinical picture has no characteristic features and is suitable for many diseases.
Cervical osteochondrosis is easy to confuse with radiculitis, hernia, and there is even a general symptomatology with a tumor of the bone system of the spine and spinal cord... So consult a specialist before starting treatment. 1
What are the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis?
It is believed that the cause of headache in one of the three cases is precisely osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The thing is that the bulk of the load falls on him and on lumbar spine. In addition to headaches, the disease has the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- neck pain radiating to the teeth;
- flies before the eyes;
- general weakness;
- feeling of numbness in the hands and shoulder girdle;
- unstable mental state, insomnia.

Please note that with cervical - chest osteochondrosis there may be cardiac signs of autonomic disorders (eg, shortness of breath).
2Why does osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occur?
First of all, the risk group includes people with a sedentary lifestyle and insufficient physical activity (physical inactivity). Of particular danger is office work, which forces you to sit in a sedentary and not always comfortable position around the clock. The load in the form of a walk to the place of work and in the opposite direction is not enough. This lifestyle leads to a weakening of the spine, poor posture.
Neck pain can occur under the influence of a number of factors:
- violation of metabolic processes in the body;
- genetic predisposition to the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- microtrauma and excessive physical stress on the spine;
- unhealthy diet, overweight;
- insufficient physical development;
- lack of vitamins, minerals;
- the presence of bad habits that lead to spasms and vasoconstriction (alcohol, smoking);
- stressful situations;
- intoxication and transferred infectious diseases.

If you have a sedentary job, you shouldn't neglect a five-minute spine warm-up. You can turn your head, do bends, or massage your neck in order to normalize blood circulation.
3Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disorder in cartilage and bone tissue, the treatment of which often does not require hospitalization. All the necessary procedures recommended by your doctor can be done at home. However, the peculiarity of the treatment lies in its duration and regularity. The wellness complex does not require large expenditures, but patience and is aimed at:
- elimination of pain with analgesics;
- strengthening metabolism in the cervical spine;
- restoration of normal blood circulation;
- improvement muscle tone neck and shoulders with exercise.
How to do massage for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Massage of cervical osteochondrosis is quite easy to master. It is not necessary to call a specialist, because you can do everything yourself. The procedure is carried out with the fingers of the hands. Massage movements are done in the direction from the spine to the periphery. No effort is needed, the action should be fluid and easy. Massage is a rubbing, kneading motion, stroking, which are best done in a sitting position.
The pose should be comfortable. It is recommended to put your legs on your legs, and on the one on top, rest your elbow. The duration of this massage is four minutes, it can be repeated several times a day. It perfectly treats osteochondrosis in pregnant women, when the use of medications is highly undesirable.

If all of these cannot be used for self-massage, it is better to contact a competent specialist who can come home. You should not trust this business to your friends or relatives. An improper effect on the cervical muscles can provoke a negative effect.
5How to cure cervical osteochondrosis using traditional medicine?
You can treat osteochondrosis at home with horseradish... It is enough to attach the sheet to the back of the neck and secure it with a bandage or any cloth at hand. It is better to do this procedure at night. By morning, the pain is significantly reduced or disappears altogether.
In the fight against osteochondrosis, the usual potato, from which you can make an ointment. To do this, grate the vegetable on a fine grater and mix with the same amount of honey. You can apply the ointment to the affected area every day, but at least once a week.

Excellent treats osteochondrosis vodka compress... To prepare it, you will need half a liter of alcohol, a gram of propolis, 50 g of mustard powder and aloe juice each. In the resulting solution, the fabric is moistened and applied to the neck for several hours, fixing the compress with a woolen scarf.
Heal the spine will help bitter pepper, which perfectly improves blood circulation. Grind two pods and cover with sunflower oil. We insist the mixture for at least four hours. Rubbing such an ointment three times a day gives a quick and long-lasting effect.
Grind 250 g of comfrey root and mix with the same amount butter... Apply to the problem area twice a day.
6What exercises are effective for cervical osteochondrosis?
You can cure cervical osteochondrosis at home yourself using the usual rolling pins... It is better to use such exercises after the end of the acute period. The patient lies down on a hard surface, puts a rope under his back and rolls it under him, paying special attention to the collar zone and neck.

You can treat cervical osteochondrosis at home using some yoga asanas... Kneel down and sit down on the floor. Clasp your hands in the lock, gently and slowly press on the head in the back of the head, smoothly bringing the chin to the chest. Perform light swinging movements for several minutes. This asana should not cause discomfort, but only slight pulling sensations.
To heal the neck at home, exercise in the same starting position will help. Raise your right hand and lightly press down on the left side of your head while swinging your left hand on the floor to maintain balance. Thus, slowly lower your head to your shoulder, and with your left hand stretch further and further, trying to completely lie on the floor. Then repeat the exercise in the opposite direction. Such exercises perfectly restore blood circulation in the cervical spine and help to strengthen the muscles.
To cure osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, an exercise therapy is recommended, which has its own characteristics for each diagnosis and has a beneficial effect on the vertebrae, helps to restore their normal functioning.
VHow to treat cervical osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis is a common pathology of the spine, characterized by dystrophic changes in the structure of the cartilaginous discs of the vertebrae and their bone base. To one degree or another, osteochondrosis manifests itself in most people after 30 years. The symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are varied, which often complicates the diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
General symptoms and signs of cervical osteochondrosis
The osteochondrosis process affects one of the parts of the spine or several at once. The lumbar and cervical vertebrae are most susceptible to pathology, as the most susceptible to stress due to the anatomy of the human skeleton. The consequences of osteochondrosis of the spine in the cervical spine deliver the most inconvenience and potential complications, because the neck is an area rich in neurovascular highways, many of which feed directly the brain.
For this reason, the clinical symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are much associated with ischemia of brain regions. In addition, the nerve roots that provide sensitivity and motor activity of the arms and shoulder girdle, when squeezed by destroyed vertebral discs, can give a varied symptomatic picture.
Signs of neck osteochondrosis depend on which of the body systems is affected by the pathology:
- Impaired blood circulation due to compression of the vertebral arteries causes most of the symptom complexes on the part of the brain.
- Compression of the roots emerging from the vertebral foramen gives a picture of peripheral nerve damage.
- Spinal cord pinching is associated with severe neurological pathologies that occur in advanced cases.
Below we will consider the general clinic of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
Pain in the back of the head, neck and collar area
This is the most common symptom. Localization of pain can be extended, affecting the shoulders, clavicular region, chest, turning into intense head migraines. The nature of the pain depends on the localization of the lesion and the severity of the pathology. At the beginning of the development of the disease, pain can be quickly transient, gradually becoming chronic, aching. At moments of exacerbation, the pain becomes shooting, with an increased tone of the neck muscles and limited head movement.
Often, pain in cervical osteochondrosis can be localized behind the sternum, in which case many patients take this symptom for angina pectoris. Differentiation can be carried out by taking a nitroglycerin tablet - the pain caused by osteochondrosis is not relieved by it.
Noise, ringing, a feeling of stuffiness in the ears
Hearing loss is often added to these symptoms. These phenomena are associated with a decrease in blood flow from the vertebral arteries to the vestibular apparatus. The complex of these symptoms is called cochlear, or cochlear syndrome, and it is far from always possible to determine its connection with osteochondrosis in the cervical spine. A specific feature for differentiation is that noise, congestion and ringing in the ears are felt when changing position, after being in the same position for a long time.
Dizziness
Vertigo is also caused by a disturbance in the blood flow to the organs of the inner ear, which ensures the balance of the body. Dizziness is often joined by nystagmus - voluntary fluctuations of the eye pupils to the sides.
Lack of air
This sensation appears due to irritation of the endings of the phrenic nerve. It is a component of the cervical nerve bundle and is involved in the regulation of breathing, its depth and frequency. Patients complain about the inability to breathe deeply. In some cases, the symptom is aggravated to severe shortness of breath and suffocation.
For the same reason, respiratory arrest at night and snoring are observed.
Lack of oxygen due to breathing problems ultimately leads to increased fatigue, decreased concentration and memory problems.
Nausea
It is accompanied by belching of air. It is also caused by problems with blood circulation in some areas of the brain and inner ear. Nausea is sometimes observed with indomitable vomiting triggered by movements of the head and body. The consequence of frequent nausea and vomiting is a decrease in appetite, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies.
Vision problems
"Flies" in the eyes, decreased visual acuity, fog in front of the eyes - these are all symptoms caused by ischemia of the part of the brain responsible for vision. Patients with osteochondrosis complain less often about vision, since the lack of blood supply from the vertebral vessels is compensated by the blood flow from the carotid artery system. Glasses and therapeutic exercises for the eye muscles do not solve the problem, usually vision improves after the treatment of osteochondrosis.
What are the most important symptoms of osteochondrosis is briefly described in this video:
Blood pressure surges
An unstable pressure level is caused by impaired blood flow in the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for the functions of the vascular-motor center.
Sudden fainting, or syncope
It occurs with spasm of the arteries of the brain due to a short-term cessation of blood flow through the vertebral arteries. The patient can be quickly brought out of the state of loss of consciousness by laying him down so that his legs are slightly higher than his head - the blood flow to the brain allows him to revive. After a fainting attack, reversible speech and movement problems may occur for some time due to a brief interruption in blood flow.
Pharyngeal symptoms
Often they can be the only sign indicating cervical osteochondrosis. Expressed as tickling, dryness and sensation, difficulty swallowing. Symptoms are associated with compression of the nerve plexuses, which are responsible for the innervation of the pharyngeal region. It is necessary to differentiate such manifestations from a similar clinic for inflammation or neoplasms.
Rise in body temperature
For cervical osteochondrosis is not the most typical symptom, it is observed rarely and locally - in the cervical and collar zone, with a slight reddening of the skin.
The clinic of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine can be, firstly, of varying severity, it depends on the stage of development of the pathology, also during periods of exacerbations they are brighter, and secondly, they develop into certain syndromes.
Symptoms depending on the stage of cervical osteochondrosis
Stage I
The beginning of degenerative processes in the cartilage of the vertebral discs. Symptoms are mild, sometimes they may not be observed at all. The first signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- Discomfort in the neck, arms, shoulders, sometimes turning into pain;
- Headache;
- Slight limitation of motor activity of the neck;
- Rapidly passing visual impairment;
- Decrease in the sensitivity of the skin of the collar zone.
Important: these symptoms become more pronounced with tilting the head.
As a rule, at this stage, patients do not go to the doctor, believing that all symptoms are associated with fatigue, stress, age, lack of sleep.
Stage II
At this stage, the protrusion of the vertebral discs began, the intervertebral fissures narrow, the collagen fiber of the fibrous ring of the disc is destroyed. There are noticeable pain symptoms of a point nature due to compression of the nerve trunks, aggravated by neck movements. Here you can already suspect cervical osteochondrosis, the symptoms of which at this stage are as follows:
- Severe neck pain, sometimes with a crunching sound;
- The skin of the shoulders and arms loses its sensitivity almost completely;
- Headaches are frequent, do not go away for a long time;
- Visual impairment with "flies" in the eyes;
- Ringing and noise in the ears;
- Weakness of the muscles of the upper limbs;
- Reduced clarity of tendon reflexes;
- Shooting pains, with recoil under the scapula;
- Feeling of a lump in your throat, trouble swallowing;
- Sleep disturbances, usually insomnia.
Holding the head in one position for a long time leads to severe pain.
At this stage of the development of the disease, patients already come to the doctor for help.
Stage III
The annulus fibrosus in the disc is destroyed, hernias are formed. There is a deformation of the spine, displacement and dislocation of the vertebrae, due to their weak fixation. Symptoms are as follows:
- Intense, acute pain in the neck, collar area, heart area;
- The sensitivity of the scalp on the back of the head, in the shoulder region, in the hands is impaired, up to complete absence;
- Hernia of the cervical spine;
- Paresis and paralysis of the upper limbs;
- Tendon reflexes are practically not observed.
This is a severe stage of the disease in which the patient is no longer able to support his head on his own. Spinal cord ischemia and compression of the spinal arteries lead to paralysis and paresis in other parts of the body and spinal stroke.
Syndromes due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The nonspecificity and a large number of various symptoms accompanying osteochondrosis of the cervical spine complicate the diagnosis and further treatment, since some of them may be a sign of completely different diseases. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are grouped together, called syndromes. Their presence and severity may indicate a pathology in the cervical spine with a specified localization.
A group of common syndromes:
Radicular... Otherwise called cervical radiculitis, it combines symptoms associated with infringement of the nerve roots of the cervical vertebrae. Characterized by "chills" in the affected area, tingling in the fingers, forearms, pasty skin, spreading to certain fingers.
Irritative-reflex... Burning and sharp pain in the back of the head and neck, sometimes with a return to the chest and shoulder, arising at the time of a change in the position of the head and neck, with sneezing and a sharp turn of the head.
Elena Malysheva and her constant assistants talk about the pain, symptoms and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in the video:
... Includes:
- headache, seizures or constantly, of a pulsating nature;
- discomfort with some movements, including after a long static position;
- weakness, nausea, loss of consciousness;
- hearing loss, balance problems;
- decreased visual acuity.
Cardiac... Almost the same picture with angina pectoris often leads to incorrect diagnosis and treatment. The syndrome appears due to irritation of the phrenic nerve receptors, partially capturing the pericardium and a large pectoral muscle... Thus, spasms in the cardiac area are more reflex, like a response to irritation of the cervical nerves. Symptoms:
- Sudden onset, prolonged pain, aggravated by a sharp movement of the neck, coughing, sneezing, which does not go away when taking heart medications.
- The ECG shows no abnormalities in the blood flow of the heart muscle.
- Sometimes there may be extrasystole and tachycardia.
Vegetative-dystonic syndrome... Subluxation of the first vertebra of the cervical spine with displacement can lead to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia. VSD is not a definite diagnosis, since it does not have pronounced symptoms. There may be neurological signs, symptoms of impaired cerebral blood flow, surges in intracranial pressure, muscle spasms. As a result, the patient's complaints are reduced to dizziness, decreased visual acuity, loss of consciousness, headaches, and nausea.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis
The described condition of the spine is a very serious pathology, which, if neglected, leads to disability, and as a result of profound disorders of cerebral circulation, to death. For this reason, self-medication in the event of such symptoms should not be dealt with. Osteochondrosis is treated in a hospital and at home, exclusively as prescribed by a doctor. At the initial stages, it is conservative, which includes medications: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthetics, hormonal agents, vitamin complexes, chondroprotectors - all this relieves inflammation, pain, and improves trophism of soft tissues and cartilage of the vertebrae.
In the acute period, drugs are prescribed in the form of injections, as the pain subsides, the patient switches to pills. To courses medicines joins physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy, usually prescribed at the stage of remission. In difficult cases, osteochondrosis is treated with surgery.
In this video you can see what a short exercise therapy course for beginners looks like:
Cervical osteochondrosis is a lesion of the vertebral discs of the cervical spine, as a result of which they undergo degenerative-dystrophic changes. The main reason for its development is a violation of the normal course of metabolic processes, which leads to a distortion of the structure of the vertebral bodies and cartilaginous discs. In the case of localization in the neck, the symptoms of pathology are largely determined by the compression of large vessels. Treatment methods are selected depending on the stage, the specificity of the course, the severity, the main symptoms.
Features of the disease
The cervical form is the most dangerous type of osteochondrosis: it leads to a deterioration in cerebral circulation, since the vertebral artery passes through this area - one of the largest vessels supplying the brain with the necessary substances and oxygen.
Displacement of the vertebrae, abnormal changes and proliferation of bone and fibrous tissue disrupt the normal functioning of the vessel.
The specificity of the symptoms of osteochondrosis in this part is determined, among other things, by one of the structural features of the cervical vertebrae, consisting in their closer adherence to one another. As a result, any change in one segment provokes the failure of the entire department.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Clinic depending on the stage
In the process of its development, cervical osteochondrosis goes through four stages. How does it manifest itself on each of them?
- Stage 1. It is characterized by the appearance of initial disturbances in the stability of the intervertebral discs. Symptoms are mild or absent. Not very pronounced pain sensations and local muscle tension are possible.
- Stage 2. Disc protrusion begins, the gaps between the vertebrae contract, the annulus fibrosus collapses. In many cases, as a result of compression of the nerve endings, pain appears - mainly of a point nature. They intensify when turning, tilting the neck. Decreases tone, weakness often appears.
- Stage 3. The process of final destruction of the fibrous ring leads to the formation of hernias. This stage is characterized by a significant deformity of the spine. Increased pain and fatigue occur against the background of sensory disorders and limited mobility in the affected area.
- Stage 4 is the most severe. Intense pain syndrome manifests itself with any attempts to move, which entails a significant limitation of the mobility of this department. At times, the pain subsides, but this does not show an improvement in the condition, but only indicates an increase in the size of bone growths, significantly limiting movement. They often lead to patient disability.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
When located in the cervical spine, the prevailing symptoms of osteochondrosis are:
 Pain is the main symptom
Pain is the main symptom - pain in the neck, back of the head, shoulder, arms;
- restriction of movements, crunching at various turns, tilting of the neck;
- weakness in the arms;
- pulling pain in the left half of the chest, radiating to the corresponding arm;
- burning sensation in the interscapular zone;
- recurrent headaches;
- weakness;
- dizziness (with a severe course of cervical osteochondrosis, it can reach loss of consciousness);
- coordination of movements is impaired, which is mainly reflected in the gait;
- hearing impairment, ringing in the ears;
- decreased vision;
- sore throat;
- poor dental health;
- weakening of the voice or its hoarseness;
- snoring is a consequence of the tension of the cervical muscles.
With the cervicothoracic type, the symptoms are almost similar to those of cervical osteochondrosis. This:
- asthenic syndrome;
- dizziness and headaches;
- periodic pressure fluctuations;
- flashing flies before the eyes;
- pain in the shoulder girdle and arms;
- muscle weakness;
- numbness, tingling, chilliness of the fingers;
- pain in the chest, heart area;
- nausea;
- numbness of the tongue, face;
- dental problems;
- sensation of current passing along the arms when trying to bend the neck.
Syndromes
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are not considered typical. Which of them are most pronounced depends largely on the specific target. Many of the manifestations can be mistakenly associated with other pathological conditions. Therefore, there are often cases when the wrong treatment is prescribed.
The complex of symptoms is divided into the following groups:
- radicular;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- irritative reflex syndrome.
 Pinched nerve endings in the neck
Pinched nerve endings in the neck Its second name is cervical sciatica. The syndrome develops as a result of pinching of the nerve endings in the cervical part. The pains are transmitted down from the neck, given to the shoulder blades, down along the shoulder on the outside of the forearm to the fingers. In this case, often appear:
- feeling of "goose bumps";
- tingling of the hand, forearm, fingers;
- pastiness.
Manifestations also vary depending on the site of the lesion. If the endings of the central nerve are affected, the pastiness extends to the thumb, middle, index fingers. When the endings of the brachial nerve are pinched, the little finger and ring finger are affected.
Irritative reflex syndrome
Its symptom is burning acute pain in the cervico-occipital region, which appears during movement after a static state: after sleep, when sneezing, a sharp turn of the head. Often the pain radiates to the shoulder and chest.
Vertebral artery syndrome
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis with it are:
- throbbing or burning headache (paroxysmal or persistent in nature), extending to the temporal region, darkening, occiput, brow ridges;
- increased discomfort with certain movements or after a prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position;
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- loss of consciousness;
- hearing problems;
- disruption of the vestibular apparatus;
- eye pain;
- deterioration of vision.
Cardiac syndrome
With the appearance of this complex of symptoms of osteochondrosis of the neck, a picture almost similar to angina pectoris develops, which often leads to erroneous treatment.
Muscle contractions and spasms in the region of the heart are most likely a reflex response to compression of the nerve endings in the lower cervical region. Cardiac syndrome is a consequence of irritation of the phrenic nerve (its fibers lead to the pericardium) or the pectoralis major muscle:
- pains appear suddenly, last a long time;
- aggravated by a sharp movement of the neck, coughing, sneezing;
- tachycardia and extrasystole are possible;
- the pain does not stop after taking coronary expansion drugs;
- there are no signs of impaired circulation on the ECG.
Exacerbation of the disease
 Cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis In the stage of exacerbation, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- increased pain and its irradiation to the scapula, interscapular zone, arms, shoulders;
- difficulty in moving the shoulders, torso, arms, sometimes breathing (inhaling and exhaling);
- pain syndrome often resembles a heart attack or intercostal neuralgia;
- when pain appears in the right hypochondrium or iliac area, the clinic is similar to the manifestations of gastritis or cholecystitis;
- headaches are of a long-term nature, there is an imbalance, visual and auditory functions;
- in the innervation zone, the trophism of the skin is disturbed, tingling, numbness, dryness, pallor, burning, chilliness appear;
- the tone of the cervical muscles increases;
- weakness, lethargy, nervous tension, anxiety, emotional instability appear;
- possible sleep disturbances, memory, problematic concentration of attention.
Osteochondrosis and vegetative vascular dystonia
Cervical osteochondrosis can lead to subluxation of the first cervical vertebra with a shift to the right or left, which provokes the development of VSD (vegetative vascular dystonia). It is quite difficult to identify it, since often there are no symptoms or they are mild. In this case, it is possible:
- squeezing of the sympathetic nerve plexuses, leading to the appearance of neurological signs or VSD;
- compression of arteries and impairment of cerebral circulation;
- compression of the veins, provoking a violation of the outflow of blood and a subsequent jump in intracranial pressure;
- compression of the spinal cord, provoking a deterioration in the movement of the cerebrospinal fluid, which also results in high pressure inside the skull;
- muscle spasm, which aggravates symptoms as a result of severe compression of blood vessels and nerves.
The results of the described processes are:
- headache;
- darkening in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- impaired visual acuity;
- double vision (diplopia);
- flashing before the eyes of "flies";
- high or low blood pressure;
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting;
- loss of consciousness.
Vertebral subluxation is detected by x-ray. Its reduction is a rather complicated procedure, usually performed under general anesthesia.
Video about the signs of cervical osteochondrosis
How is the disease diagnosed?
The leading methods for diagnosing cervical osteochondrosis are:
- radiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- ultrasound dopplerography;
- duplex scanning.
The last two methods are used to check the condition of the vessels in the neck.
